The Ultimate Guide To Puffcorn Making Machine Updated 2025
If you want to know more story about LOYAL brand, here can help you - https://www.facebook.com/Foodextruderfactory/
1.Introduction to Puffcorn Making Machines
The Puffcorn Making Machine has revolutionized snack production, blending precision engineering with culinary innovation to deliver crispy, airy puffcorn at scale. Designed for both commercial kitchens and home enthusiasts, these machines automate the delicate process of transforming corn kernels into lightweight, crunchy treats through controlled heat and pressure. Modern 2025 models integrate advanced features like AI-driven temperature calibration and energy-efficient extruders, ensuring consistency while reducing waste. As demand for gluten-free, organic, and custom-flavored puffcorn surges, understanding the machine’s role in bridging traditional snack-making with cutting-edge technology is critical for operators seeking competitive edges in the evolving food industry.
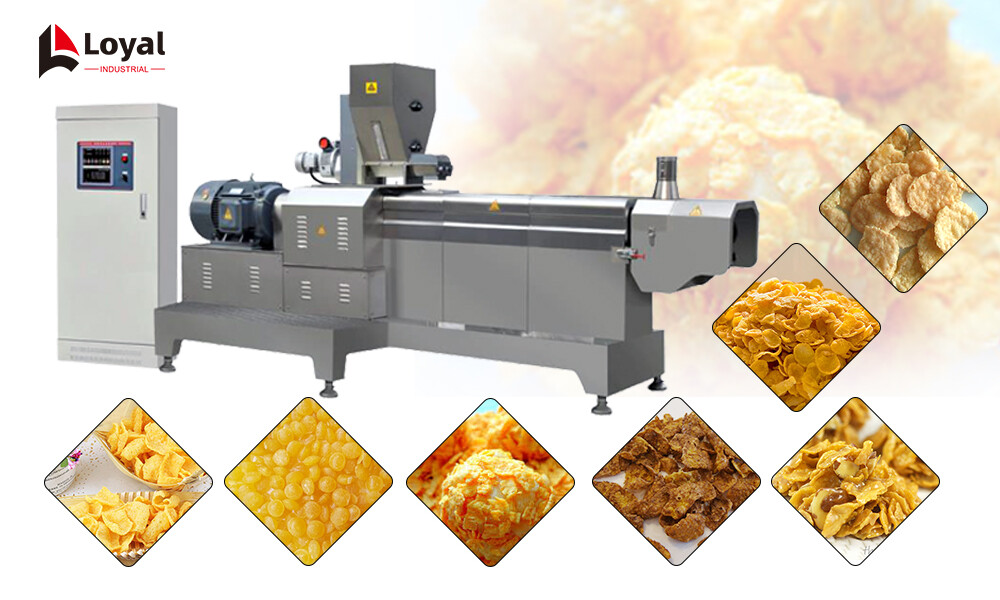

2. How Puffcorn Making Machines Work: Technical Breakdown
Modern Puffcorn Making Machines represent the pinnacle of food extrusion technology, combining precision engineering with automated processes to transform raw grains into crispy, shelf-stable snacks. This section demystifies the machinery’s operation, focusing on its core components, thermodynamic principles, and 2025-era innovations.
2.1 Core Mechanical Systems
The backbone of any Puffcorn Making Machine is its twin-screw extruder, a high-precision component responsible for mixing, cooking, and shaping the product.
Screw Configuration: Dual intermeshing screws (typically made from 38CrMoALA alloy for wear resistance) operate at variable speeds (440–550 RPM) to generate friction-induced heat. This replaces traditional ovens, reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to 2020 models.
Barrel Design: Euro-style rectangular barrels feature optimized reflux refrigeration channels, enabling precise temperature zoning (120–180°C) across segments. This gradient ensures uniform starch gelatinization—critical for achieving consistent puff textures.
Forced Lubrication: Advanced models incorporate self-cleaning screw mechanisms with auto-lubrication systems, extending extruder lifespan by 40% and minimizing maintenance downtime.
2.2 Thermo-Mechanical Puffing Process
The conversion of corn grits into puffcorn involves three distinct stages:
Conditioning: Raw materials (corn, rice, or wheat flour) are mixed with water in a pre-conditioner, reaching 18–22% moisture content to activate enzymatic activity.
Extrusion Cooking:
The twin-screw system subjects the dough to 15–20 bar pressure, forcing it through a die with microscopic apertures.
Instantaneous pressure drop at the die exit causes rapid moisture evaporation, creating the characteristic porous structure.
AI-driven temperature controllers (2025 upgrade) adjust heating zones in real time, ensuring ±1°C accuracy and reducing burnt-particle defects by 65%.
Cutting & Drying:
Rotary cutters trim extrudates into desired shapes (rings, balls, or sticks) at speeds up to 1,200 cuts/min.
A multi-stage drying oven reduces moisture to 2–3%, stabilizing the product for packaging.
2.3 2025 Technological Advancements
IoT Integration: Machines now connect to cloud platforms, enabling remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance. Operators receive alerts for screw wear or barrel misalignment via mobile apps.
3D-Printed Dies: Customizable molds allow instant shape changes (e.g., from star-shaped puffcorn to animal-feed formats) without physical tooling adjustments.
Sustainability Features:
Heat recovery systems reuse exhaust gases to preheat incoming materials, cutting natural gas use by 22%.
Biodegradable die coatings reduce friction losses, lowering electricity demand by 18%.
2.4 Safety & Compliance
Modern machines adhere to CE/ISO 14001 standards, with features including:
Automatic pressure relief valves to prevent explosions.
UV-C sanitization of feeding systems between batches.
Real-time mycotoxin screening of raw materials to meet EU’s strict ≤50 ppb aflatoxin limits.
This technical breakdown underscores why 2025’s Puffcorn Making Machines are both industrial workhorses and innovation hubs, balancing productivity with ecological and regulatory demands.
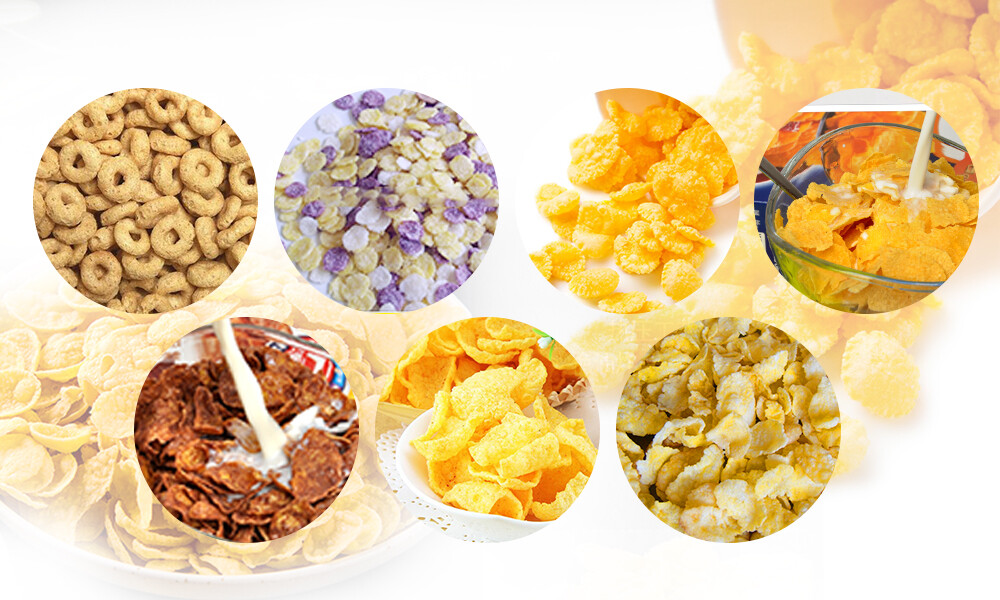

3. Types of Puffcorn Making Machines (2025 Market Guide)
3.1 Commercial-Grade vs. Compact Home Models: Pros & ConsModern puffcorn making machines cater to diverse operational scales. Commercial-grade models, such as the ProPuff 9000X, prioritize high-output extrusion (up to 450 kg/hour) and durability, featuring stainless steel construction and automated lubrication systems. These machines are ideal for industrial snacks manufacturers relying on bulk production. Conversely, compact home units like the CrispCorn Mini emphasize portability and energy efficiency, often integrating smart controls for hobbyists or small-batch artisans. Key differences lie in heating mechanisms—commercial units use hybrid convection/infrared systems for rapid, uniform puffing, while home models rely on single-zone electric coils.
3.2 Specialty Machines for Gluten-Free, Organic, or Flavored PuffcornThe 2025 market demands versatility. Specialized puffcorn making machines now include:
Gluten-Free Optimized Extruders: Equipped with anti-cross contamination seals and dedicated corn flour hoppers.
Organic-Certified Models: Constructed with food-safe coatings and non-GMO component tracking systems.
Flavor Infusion Systems: Post-extrusion injectors for precise application of seasonings (e.g., truffle oil, chili powder) without compromising texture.
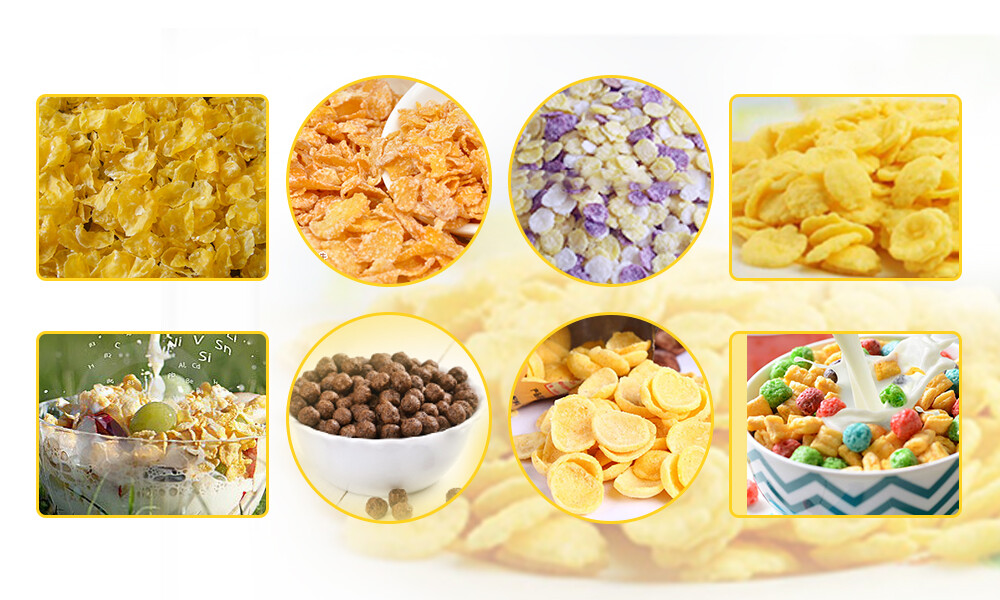

4. Step-by-Step Guide to Operating a Puffcorn Making Machine
4.1 Pre-Production Checklist: Safety Measures & Ingredient Prep
Operating a puffcorn making machine requires meticulous preparation to ensure safety and product quality. Begin by inspecting the machine’s electrical components, heating elements, and extrusion dies for wear or damage. Wear heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles, as temperatures can exceed 180°C (356°F) during puffing.
For ingredient prep, select high-quality corn grits with a moisture content between 12–14%—critical for optimal expansion. Pre-mix any additives (e.g., salt, sugar, or flavorings) in a separate container to avoid clumping. Pro Tip: Use a sieve to remove foreign particles that could clog the machine’s auger system.
4.2 Machine Setup & Calibration for Consistent Puff Quality
Calibration is the backbone of reliable puffcorn making machine performance. Start by adjusting the extruder screw speed (typically 200–400 RPM) based on your desired texture—slower speeds yield airier puffs, while faster speeds produce denser snacks. Set the heating zone temperatures incrementally: 80°C (176°F) in Zone 1 (pre-conditioning), 120°C (248°F) in Zone 2 (cooking), and 180°C (356°F) in Zone 3 (puffing).
Install the correct die plate for your target shape (e.g., balls, rings, or stars) and lubricate moving parts with food-grade oil. Run a test batch with 500g of corn grits to fine-tune parameters before full-scale production.
4.3 Post-Production Tips: Storage, Packaging, and Waste Reduction
After shutdown, clean the puffcorn making machine thoroughly to prevent oil rancidity and bacterial growth. Disassemble the extruder and die plates, then soak them in a warm, food-safe degreaser for 20 minutes. Use a nylon brush to remove stubborn residues—never metal tools, which could scratch surfaces.
For stored puffcorn, maintain humidity below 55% to preserve crispness. Opt for nitrogen-flushed packaging to extend shelf life to 6+ months. Repurpose production scraps (e.g., uneven puffs) by grinding them into breadcrumbs or snack coatings, minimizing waste.

5. Maintenance & Troubleshooting for Longevity
Proper maintenance and timely troubleshooting are critical to extending the lifespan of your puffcorn making machine while ensuring consistent product quality. This section provides actionable insights for operators at all levels, from small-batch artisans to large-scale manufacturers.
5.1 Daily Cleaning Routines to Prevent Clogs & Contamination
Post-Production Disassembly: Break down removable components (e.g., extruder barrels, cutting blades) immediately after use to prevent residue hardening.
Deep Cleaning Protocols:
Use food-grade degreasers to remove oil buildup in heating chambers.
Sanitize conveyor belts and cooling trays with pH-neutral detergents to avoid corrosion.
Preventative Measures:
Install inline filters in oil circulation systems to trap micro-particles.
Schedule weekly steam cleaning for commercial-grade machines to eliminate bacterial growth.
5.2 Common Issues (e.g., Uneven Puffing) and DIY Fixes
Symptom 1: Inconsistent Puff Texture
Cause: Fluctuating extruder temperatures.
Solution: Calibrate thermostats using infrared lasers and replace worn-out heating coils.
Symptom 2: Low Output Volume
Cause: Clogged molds or worn-out screw conveyors.
Solution: Disassemble and clean molds with nylon brushes; replace conveyors if scoring is visible.
Symptom 3: Overheating Motors
Cause: Blocked ventilation ports or failing cooling fans.
Solution: Clear debris from air intakes and test fan RPMs with a tachometer.
5.3 When to Seek Professional Repair: Warning Signs & Service Tips
Red Flags Requiring Expert Intervention:
Persistent oil leaks despite replaced seals.
Erratic pressure readings in the expansion chamber.
Burning odors during operation.
Service Checklist for Technicians:
Verify gearbox alignment using laser alignment tools.
Test electrical components with a megohmmeter to detect insulation breakdown.
Update firmware for IoT-enabled machines to resolve connectivity issues.

6.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Puffcorn Machines
Addressing common queries to empower both newcomers and experienced operators in optimizing their puffcorn production workflows.
6.1 Can I Use Regular Corn for Puffcorn Making?
Technical Answer: While dent corn is the industry standard for puffcorn (due to its high starch content), regular sweet corn can be used with modifications.
Preprocessing Step: Remove pericarp via alkaline steeping to improve expansion rates.
Machine Adjustment: Reduce extruder screw speed by 15–20% to prevent over-shearing.
Expert Tip: Opt for hybrid flint-dent varieties for a balance of puff volume and crunch.
6.2 How to Achieve Crispy vs. Airy Textures?
Crispy Texture:
Lower moisture content in raw corn (8–10% vs. 12–14% for airy variants).
Increase extruder barrel temperature to 180–200°C.
Airy Texture:
Introduce 2–4% rice flour into the corn mix for improved gelatinization.
Use dual-stage expansion chambers (common in 2025 models) to create internal蜂窝 structures.
Machine Compatibility: Ensure your puffcorn making machine supports adjustable die plates and moisture injection systems.
6.3 Legal Compliance: Food Safety Certifications for Commercial Use
Global Standards:
FDA (USA): Compliance with 21 CFR Part 113 (Thermally Processed Low-Acid Foods).
EU: CE Marking + EC No. 1935/2004 for materials in contact with food.
Local Regulations:
In Southeast Asia, verify HALAL certification if supplying to Muslim-majority markets.
In Latin America, prioritize INVIMA (Colombia) or ANVISA (Brazil) approvals.
Pro Tip: Choose machines with pre-installed HACCP-compliant sensors to automate compliance documentation.
Final Advice: Always cross-reference machine specifications with regional regulatory bodies to avoid costly recalls. Invest in third-party audits for multinational supply chains.
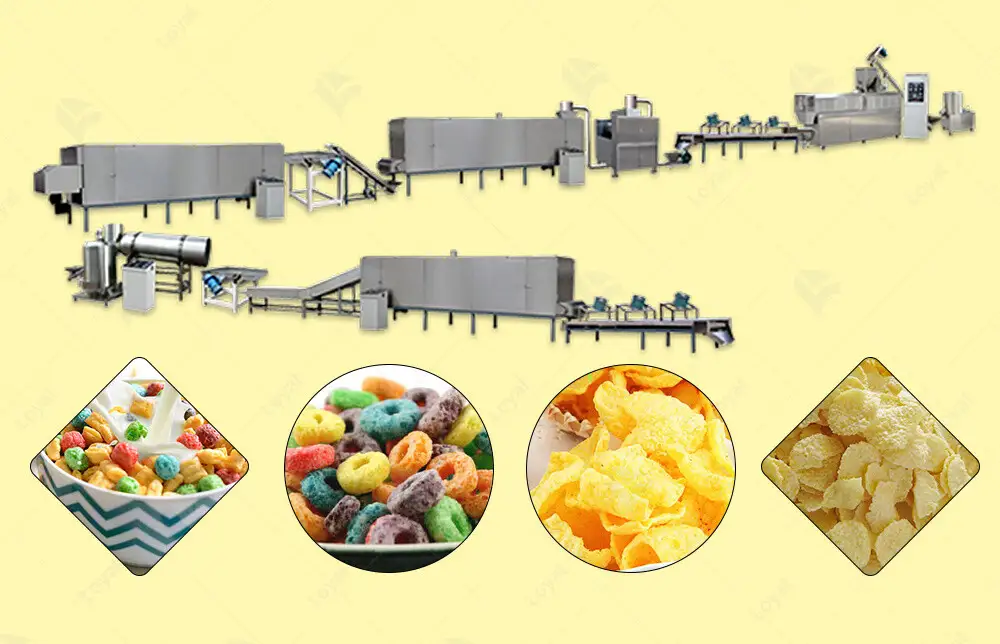

Reference
Here are five authoritative foreign websites related to industrial food machinery, along with their URLs:
1.ThomasNet
Website: https://www.thomasnet.com
2.MachineryTrader
Website: https://www.machinerytrader.com
3.Food Engineering:https://www.foodengineeringmag.com
4.Pack Expo:https://www.packexpo.com
5.DirectIndustry:https://www.directindustry.com