Everything you Need to Know About Food Extruder
Understanding Food Extrusion Technology
Food extrusion technology is a pivotal process in the food industry, revolutionizing the way various food products are manufactured. At its core, food extrusion involves the conversion of raw ingredients into finished products through a mechanical and thermal process. This process typically entails forcing a mixture of ingredients through a die to form a desired shape and texture.
Food extruders utilize advanced machinery and precise control systems to achieve consistent results. They are commonly employed in the production of a wide range of food items, including breakfast cereals, snacks, pasta, pet food, and textured vegetable protein (TVP). The versatility of food extrusion technology allows manufacturers to create products with diverse shapes, sizes, colors, and flavors to meet consumer preferences.
One of the key advantages of food extrusion is its ability to efficiently process various ingredients, including grains, starches, proteins, and additives. The extrusion process can modify the physical and chemical properties of these ingredients, resulting in enhanced nutritional value, improved texture, and extended shelf life. Additionally, food extrusion offers flexibility in product formulation, enabling manufacturers to innovate and develop new recipes to cater to evolving consumer demands.
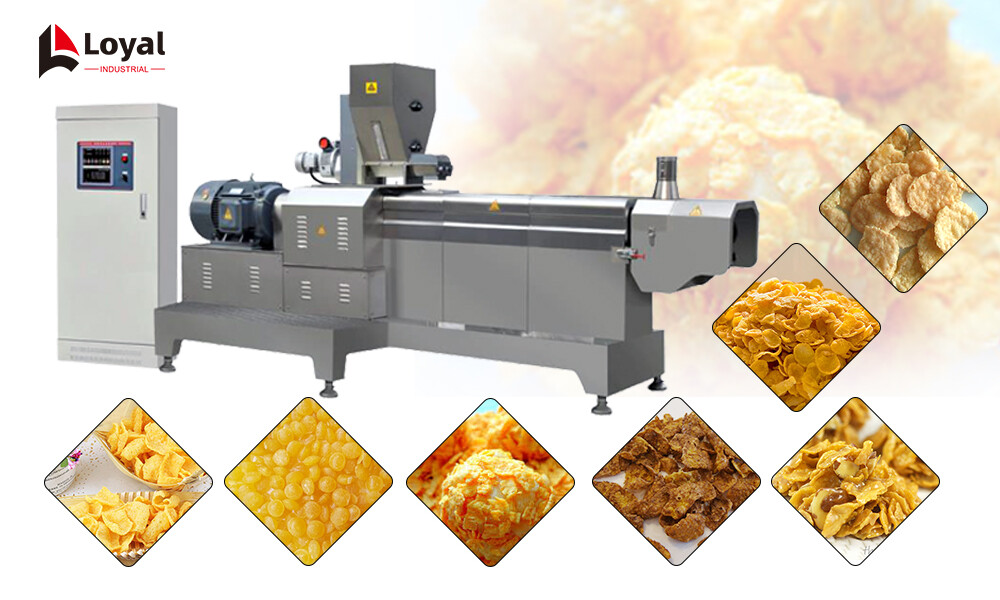

Exploring Industrial Food Extruder Types
Industrial food extruders come in a variety of types, each tailored to specific applications and production requirements. One common classification is based on the design and configuration of the extrusion system, which can include single-screw, twin-screw, and multi-screw extruders.
Single-screw extruders are the simplest and most widely used type, featuring a single rotating screw housed within a barrel. These extruders are suitable for processing a wide range of ingredients and are often employed in the production of snacks, cereals, and pasta. They offer relatively low capital investment and operational costs, making them ideal for small to medium-scale manufacturing operations.
Twin-screw extruders, on the other hand, utilize two intermeshing screws to convey and knead the ingredients within the extrusion chamber. This design provides greater flexibility and control over the extrusion process, allowing for precise temperature and pressure adjustments. Twin-screw extruders are commonly used in the production of high-value products such as pet food, aquafeed, and meat analogs.
Multi-screw extruders, including co-rotating and counter-rotating configurations, are employed in specialized applications that require high throughput and intensive mixing capabilities. These extruders are commonly used in the production of textured vegetable protein (TVP), breakfast cereals, and functional ingredients.

Components and Features of Modern Food Extruders
Modern food extruders comprise several key components and features that contribute to their efficiency and effectiveness in food processing operations. One essential component is the extrusion barrel, which houses the screw(s) responsible for conveying and compressing the ingredients. Barrels are typically constructed from stainless steel to withstand high temperatures and pressures encountered during extrusion.
The screws within the extruder play a crucial role in mixing, shearing, and shaping the food materials as they move through the barrel. Depending on the desired outcome, screws may feature different profiles, pitches, and configurations to achieve specific processing objectives. Additionally, advanced screw designs may incorporate elements such as reverse flighting or self-cleaning features to enhance performance and reduce downtime.
Temperature control systems are another critical feature of modern food extruders, allowing precise regulation of heat throughout the extrusion process. This ensures that ingredients are cooked or processed to the desired degree, while also maintaining food safety and quality standards. Temperature sensors and control mechanisms help monitor and adjust heating zones within the extruder to achieve optimal processing conditions.
Furthermore, modern food extruders often include advanced control systems equipped with user-friendly interfaces for monitoring and managing the extrusion process. These systems may offer features such as recipe management, data logging, and real-time performance monitoring to facilitate operation and troubleshooting. Integration with automation and data analysis tools can further enhance productivity and quality control in food manufacturing operations.
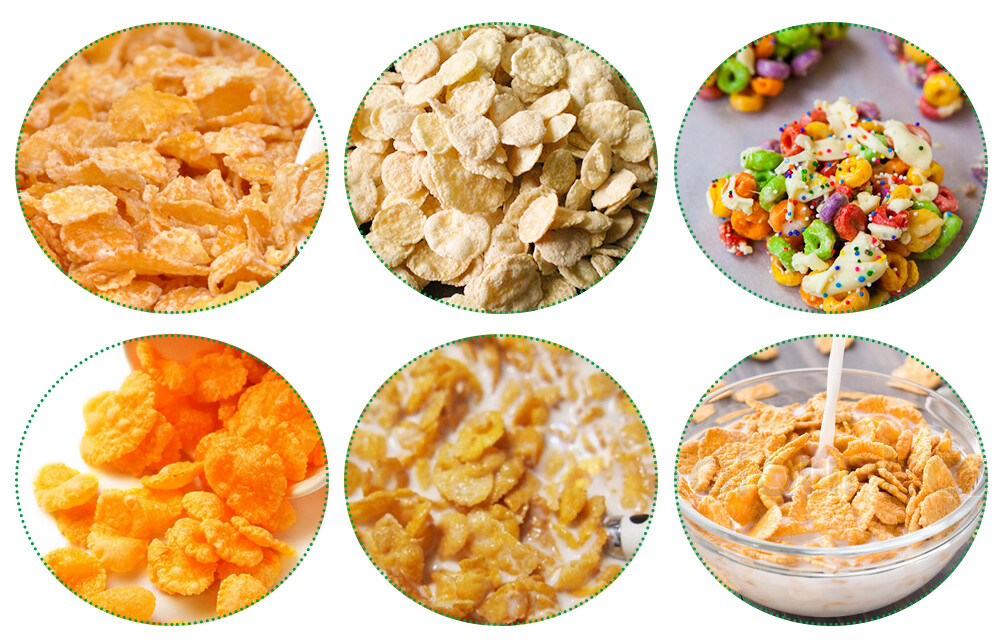

Key Considerations for Selecting Better Equipment
When choosing between food extruders from different manufacturers, such as those offered by LOYAL and Coperion, several factors need to be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific production needs. Below, we'll compare these two manufacturers' food extruders in five key aspects: design, capacity, versatility, reliability, and support.
| Aspect | LOYAL Food Extruder | Coperion Food Extruder |
| Design | Compact design with streamlined components, suitable for small to medium-scale operations. | Robust and modular design featuring advanced control systems, ideal for large-scale industrial applications. |
| Capacity | Offers moderate to high throughput rates, suitable for small to medium-sized production lines. | Provides high-capacity extrusion capabilities, catering to large-scale manufacturing facilities with high production demands. |
| Versatility | Versatile in processing a wide range of ingredients, including grains, cereals, and snacks. | Highly versatile with customizable configurations to accommodate various product formulations and processing requirements. |
| Reliability | Known for reliable performance with consistent product quality and minimal downtime. | Renowned for robust construction and dependable operation, ensuring continuous production even under demanding conditions. |
| Support | Provides comprehensive technical support and after-sales service to assist customers with installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. | Offers extensive customer support network, including training programs and remote assistance, to optimize equipment performance and efficiency. |
Considering these factors, manufacturers can make informed decisions based on their specific production needs, budget constraints, and long-term operational objectives. Whether opting for a LOYAL or Coperion food extruder, it's essential to prioritize reliability, efficiency, and manufacturer support to maximize return on investment and ensure seamless production processes.
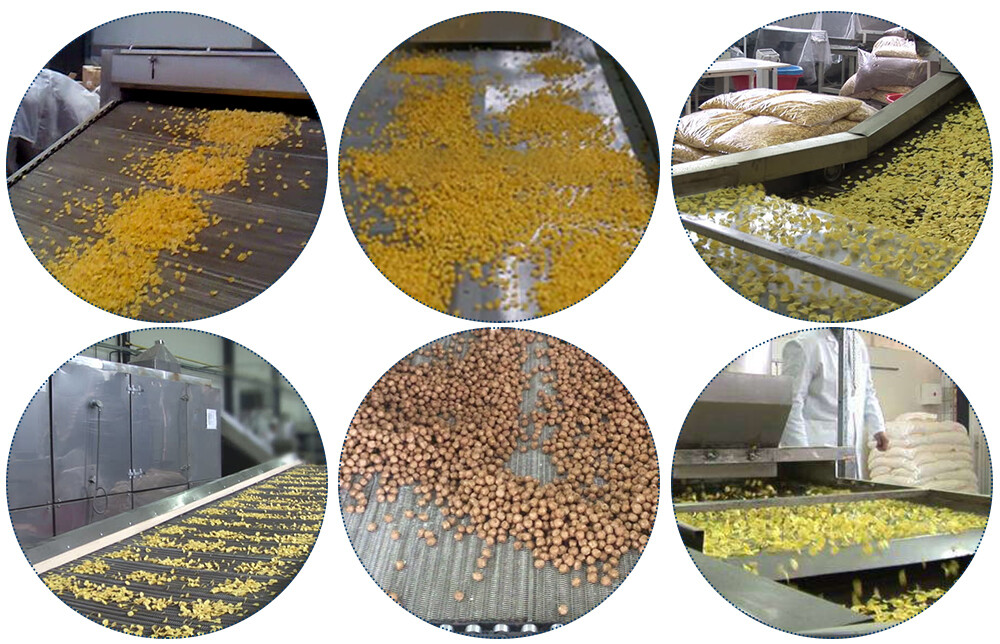

Operational Insights: Maximizing Efficiency
Efficiency is paramount in the operation of food extruders to ensure optimal productivity and resource utilization. To maximize efficiency, several key strategies and operational insights can be implemented.
Firstly, it is essential to maintain regular maintenance schedules for food extrusion equipment. Routine inspections and preventive maintenance tasks, such as lubrication of moving parts and replacement of worn components, help to minimize downtime and prolong the lifespan of the machinery. Additionally, calibration and optimization of process parameters, including temperature, pressure, and screw speed, are crucial for achieving consistent product quality and throughput.
Furthermore, investing in advanced control systems and automation technologies can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Real-time monitoring and control of extrusion parameters allow for timely adjustments to optimize performance and minimize energy consumption. Moreover, integration with data analytics platforms enables predictive maintenance and process optimization based on historical performance data.
Collaboration with suppliers and equipment manufacturers is another valuable strategy for maximizing efficiency in food extrusion processes. Engaging in continuous training programs and technical support services ensures that operators are well-equipped with the knowledge and skills required to operate the equipment effectively. Additionally, leveraging supplier expertise for process optimization and troubleshooting can help address challenges and streamline operations.
In summary, maximizing efficiency in food extrusion processes requires a combination of proactive maintenance practices, advanced control systems, and collaboration with suppliers. By implementing these strategies and operational insights, manufacturers can achieve higher productivity, consistent product quality, and reduced operating costs.

Safety Measures in Food Extrusion Processes
Safety is paramount in food extrusion processes to protect both personnel and equipment from potential hazards and risks. Implementing comprehensive safety measures is essential to ensure a safe working environment and prevent accidents or injuries.
One of the primary safety considerations in food extrusion processes is the proper design and installation of equipment. Ensuring that extruders are equipped with safety guards, emergency stop mechanisms, and interlock systems helps to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate risks during operation. Additionally, implementing proper ventilation systems and fire suppression measures reduces the risk of combustion or overheating in the production area.
Furthermore, providing adequate training and safety protocols for personnel operating food extrusion equipment is crucial. Operators should be trained in equipment operation, maintenance procedures, and emergency response protocols to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries. Additionally, implementing strict hygiene practices and personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements helps to prevent contamination and ensure food safety compliance.
Regular safety inspections and audits are also essential to identify and address potential hazards in food extrusion processes. Conducting hazard assessments, risk analyses, and safety audits enable proactive identification of safety issues and implementation of corrective actions to mitigate risks. Moreover, fostering a culture of safety and continuous improvement encourages employees to actively participate in safety initiatives and contribute to a safer work environment.
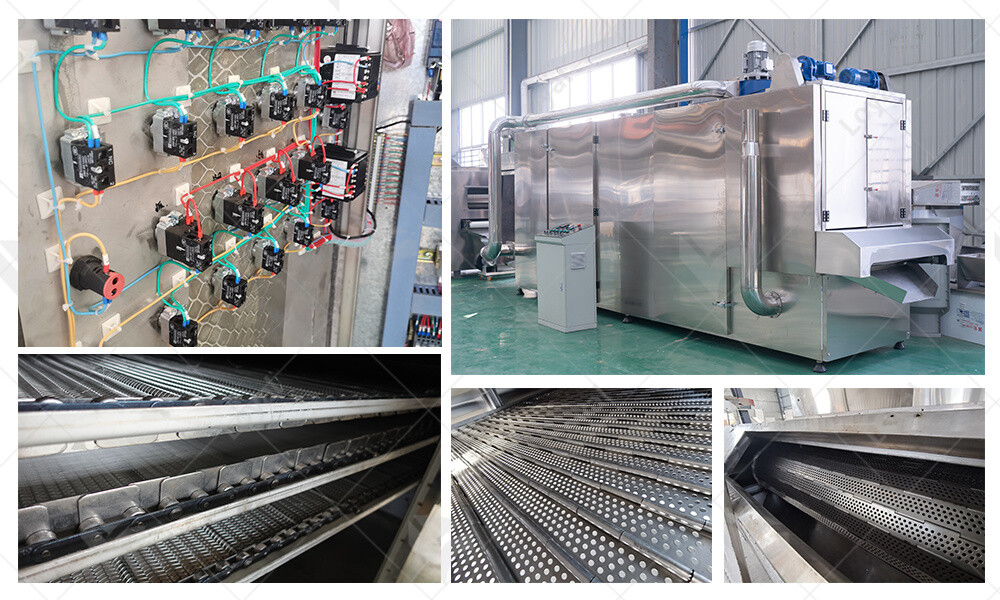

Quality Assurance and Control Methods
Quality assurance and control are paramount in the food industry to ensure the safety, consistency, and integrity of food products. When it comes to food extrusion processes, implementing effective quality assurance and control methods is crucial to meeting regulatory standards and consumer expectations.
One key method for quality assurance in food extrusion is process monitoring. This involves continuously monitoring various parameters such as temperature, pressure, moisture content, and flow rate throughout the extrusion process. Advanced sensors and control systems are utilized to maintain optimal conditions and detect any deviations from the desired parameters in real-time. By closely monitoring the process variables, manufacturers can identify and rectify issues promptly, thereby ensuring consistent product quality.
In addition to process monitoring, product testing and analysis play a vital role in quality assurance. Samples of extruded products are subjected to rigorous testing to evaluate their physical, chemical, and sensory properties. This may include tests for texture, color, density, moisture content, nutritional composition, and microbiological safety. Analytical techniques such as microscopy, spectroscopy, chromatography, and microbiological assays are employed to assess product quality and identify any potential contaminants or defects.
Furthermore, implementing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) principles is essential for quality assurance in food extrusion. GMP guidelines ensure that production facilities adhere to strict hygiene and sanitation standards, preventing contamination and ensuring product safety. HACCP protocols involve identifying and controlling potential hazards at critical points in the production process to mitigate risks and uphold product quality. By integrating these practices into food extrusion operations, manufacturers can establish robust quality assurance systems and uphold the highest standards of product quality and safety.
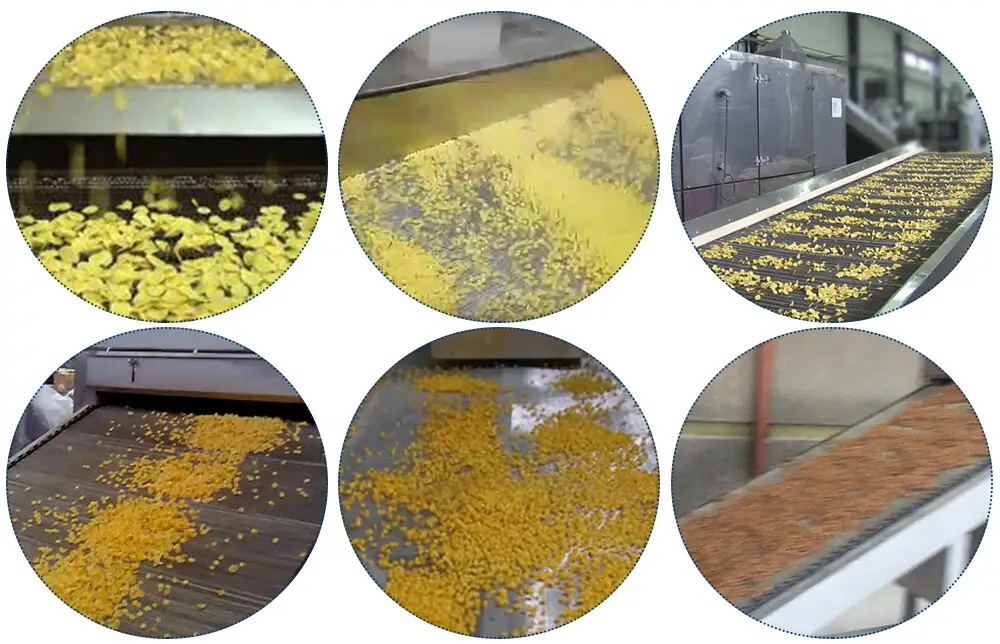

Enhancing Product Development with Food Extruders
Food extrusion technology offers vast opportunities for product development and innovation in the food industry. By leveraging the versatility and capabilities of food extruders, manufacturers can create a wide range of novel and value-added products to meet consumer preferences and market demands.
One way to enhance product development with food extruders is by experimenting with different ingredient formulations and processing parameters. Food scientists and engineers can explore the use of various grains, legumes, proteins, fats, and additives to develop unique textures, flavors, and nutritional profiles. By adjusting parameters such as extrusion temperature, screw speed, die configuration, and moisture content, manufacturers can tailor the characteristics of extruded products to achieve desired attributes such as crispiness, chewiness, and shelf stability.
Moreover, food extrusion enables the incorporation of functional ingredients and additives to enhance the nutritional value and functional properties of food products. Ingredients such as vitamins, minerals, fibers, antioxidants, and prebiotics can be efficiently incorporated into extruded products to offer health benefits and cater to specific dietary requirements. Additionally, encapsulation techniques can be employed to protect sensitive bioactive compounds and ensure their stability during processing and storage.
Furthermore, food extrusion allows for the creation of textured vegetable proteins (TVP), meat analogs, and plant-based alternatives to meat and dairy products. By extruding plant-based ingredients such as soy, peas, and wheat gluten, manufacturers can produce meat-like textures and flavors that appeal to vegetarians, vegans, and health-conscious consumers. These innovative products offer sustainable and ethical alternatives to traditional animal-derived foods, contributing to the growing trend of plant-based eating.
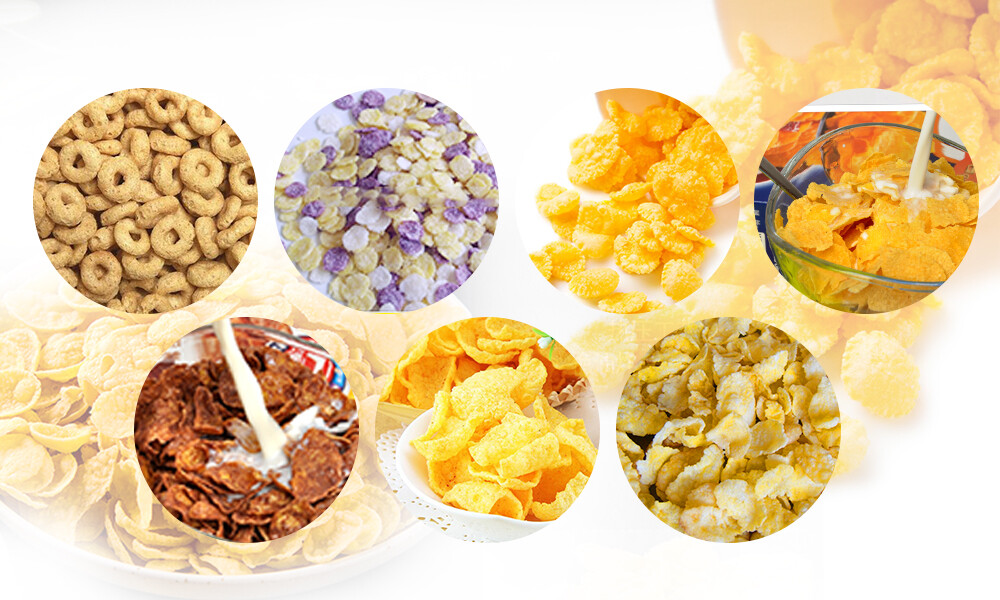

Environmental Impact and Sustainability Practices
Environmental sustainability is a critical consideration in the food extrusion industry, as manufacturers strive to minimize their ecological footprint and promote responsible production practices. Several key initiatives are being implemented to address environmental concerns and enhance sustainability within the food extrusion sector.
Firstly, there is a growing emphasis on energy efficiency in food extrusion processes. Manufacturers are investing in advanced technologies and equipment that reduce energy consumption and optimize resource utilization. This includes the development of more efficient extruder designs, as well as the implementation of process control systems that regulate temperature, pressure, and other parameters to maximize energy efficiency.
There is a concerted effort to reduce waste generation and promote recycling in food extrusion operations. This involves the utilization of by-products and co-products from the extrusion process as feedstock for other applications, such as animal feed or biofuel production. By implementing closed-loop systems and waste reduction strategies, manufacturers can minimize their environmental impact and achieve greater sustainability in their operations.
The adoption of sustainable sourcing practices is becoming increasingly important in the food extrusion industry. Manufacturers are seeking out suppliers that adhere to responsible agricultural practices, including sustainable farming methods and ethical labor standards. By sourcing raw materials from certified suppliers and promoting transparency throughout the supply chain, manufacturers can ensure the sustainability of their products from farm to fork.
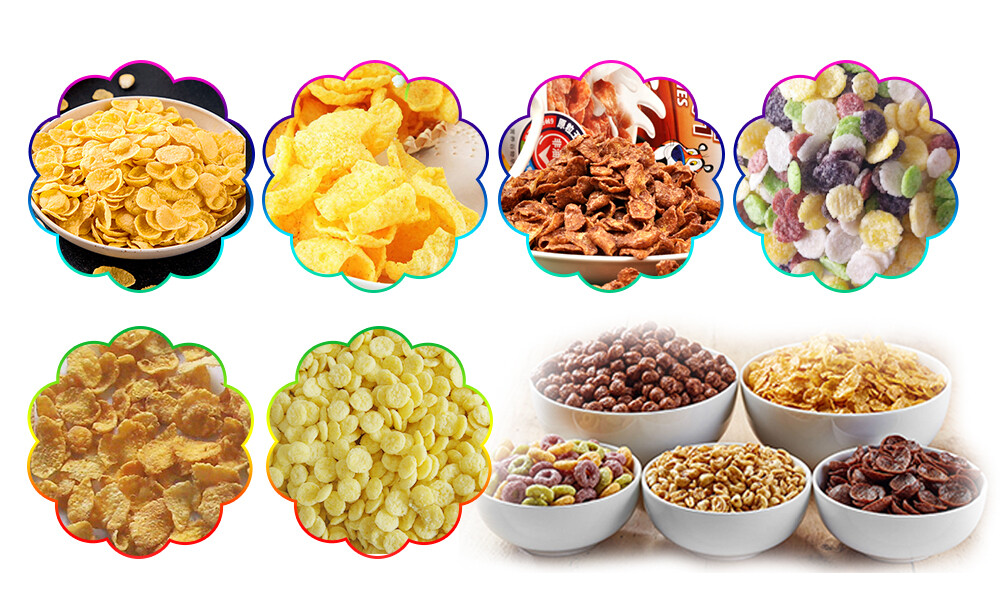

Future Prospects and Innovations in Food Extrusion Industry
The future of the food extrusion industry holds exciting prospects and innovations as manufacturers continue to push the boundaries of technology and product development. Several trends and advancements are shaping the trajectory of the industry, driving innovation and opening up new opportunities for growth and expansion.
One key area of focus is the development of novel ingredients and formulations to meet evolving consumer preferences and dietary trends. Manufacturers are exploring alternative protein sources, functional ingredients, and plant-based formulations to cater to the growing demand for healthier and more sustainable food options. This includes the production of plant-based meat alternatives, fortified snacks, and gluten-free products using advanced extrusion technology.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on customization and personalization in the food extrusion industry. Manufacturers are leveraging advanced processing techniques and digital technologies to tailor products to individual consumer preferences and dietary requirements. This includes the use of 3D printing technology to create customized food shapes and textures, as well as the development of personalized nutrition solutions based on genetic and metabolic profiling.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics is revolutionizing food extrusion processes, enabling manufacturers to optimize production efficiency, quality control, and product innovation. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, providing insights into process optimization, predictive maintenance, and product development.
References
1. Food Engineering Magazine
Website: [https://www.foodengineeringmag.com/]
2. Food Processing Magazine
Website: [https://www.foodprocessing.com/]
3. Institute of Food Technologists (IFT)
Website: [https://www.ift.org/]
4. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE)
Website: [https://www.asabe.org/]
5. European Federation of Food Science and Technology (EFFoST)
Website: [https://effost.org/]

FAQs: Common Questions about Food Extruders
1. What is a food extruder?
A food extruder is a machine used in the food industry to process various ingredients by forcing them through a die to create a specific shape or texture. It's commonly used to produce snacks, cereals, pasta, and pet food.
2. How does a food extruder work?
A food extruder operates by feeding a mixture of ingredients into a chamber where they are heated and compressed by a rotating screw. The pressure generated forces the mixture through a die, shaping it into the desired form. The extruded product is then cut to the desired length and cooled for further processing.
3. What are the benefits of using a food extruder?
Food extruders offer several advantages, including the ability to process a wide range of ingredients, uniform product quality, high production efficiency, and versatility in creating different shapes and textures. They also enable precise control over processing parameters, leading to consistent results and improved product shelf life.
4. What types of products can be made with a food extruder?
Food extruders can be used to produce a variety of products, including snacks, breakfast cereals, pasta, pet food, textured vegetable protein (TVP), and functional ingredients. The versatility of food extrusion technology allows for the creation of diverse products to meet consumer preferences and market demands.