The Ultimate Guide to Microwave Dryer Machine in 2024
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of food processing technology, microwave dryer machines have emerged as indispensable tools for achieving efficient and high-quality drying processes. As we delve into "The Ultimate Guide to Microwave Dryer Machine in 2024," it becomes evident that the advancements in microwave technology have revolutionized the way we dry food products.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore the working principles, applications, challenges, and future trends of microwave dryer machines in the context of the food processing industry in 2024. Join us as we embark on a journey to uncover the intricacies of this innovative technology and its profound impact on food production and quality assurance.

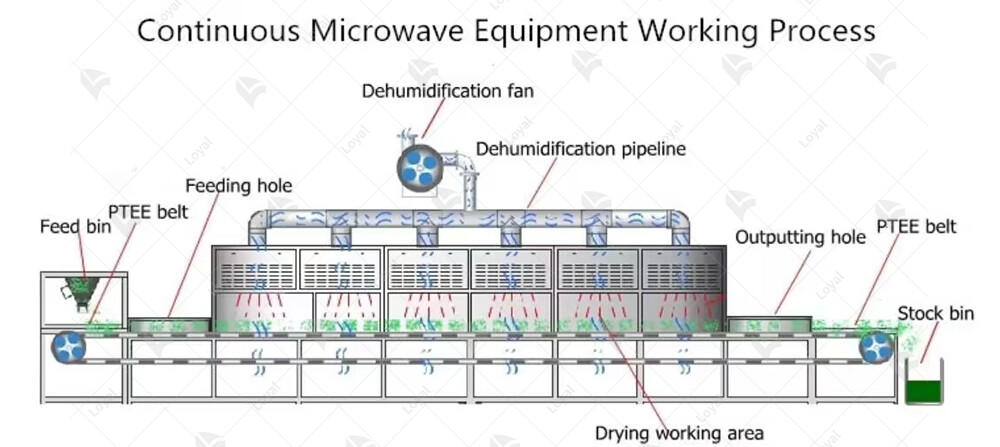
Working principle of microwave dryer
Microwave dryers work on the principle of dielectric heating, using electromagnetic waves in the microwave frequency range to generate heat within the material being dried. Unlike conventional dryers that rely on convection or conduction, microwave dryers penetrate the material and directly heat the water molecules present. The key component of a microwave dryer is the magnetron, which generates microwaves with a frequency of typically 2450 MHz. These microwaves are then emitted into the drying chamber, where they interact with the water molecules in the material. When exposed to microwave radiation, the water molecules align with the alternating electric field of the microwaves, causing them to oscillate rapidly. This oscillation generates frictional heat within the material, causing the water to evaporate quickly. One of the advantages of microwave dryers is their ability to heat the material evenly from the inside out. This can shorten drying time and maintain product quality by minimizing thermal damage and preserving its natural properties. In summary, the working principle of a microwave dryer is to generate electromagnetic waves that cause the water molecules within the material to oscillate rapidly, resulting in efficient and uniform drying.

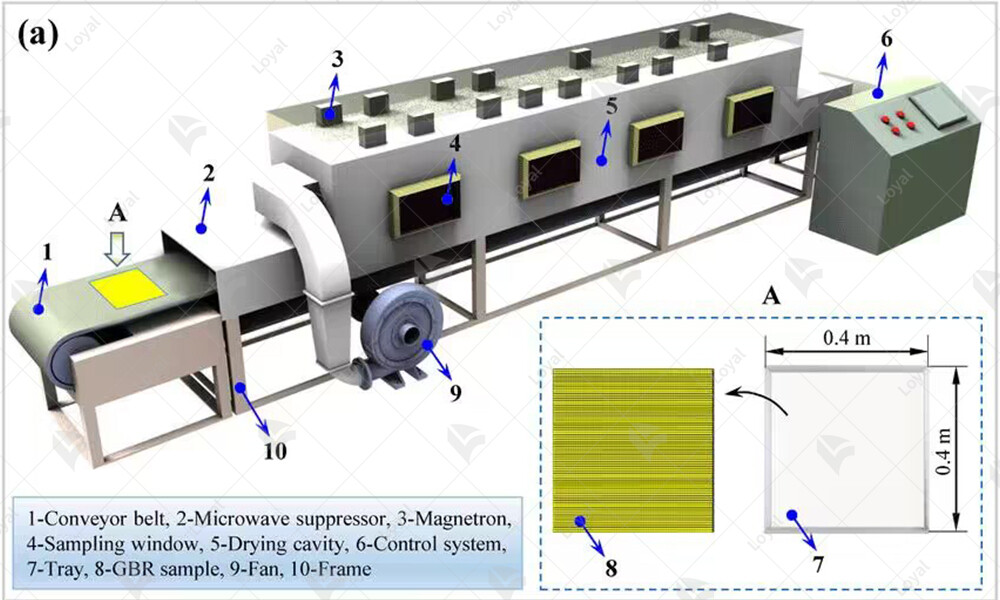
Key Components of Microwave Dryer
Microwave dryer machines, at their core, consist of several key components that work together seamlessly to facilitate the drying process. Understanding these components is essential for grasping the functionality and efficiency of microwave drying technology.
1. Magnetron:
The magnetron serves as the heart of the microwave dryer machine. It generates the microwave radiation required for heating the product. This high-powered electronic vacuum tube converts electrical energy into electromagnetic waves, which are then emitted into the drying chamber.
2. Waveguide System:
The waveguide system is responsible for directing the microwave radiation from the magnetron to the drying chamber. It consists of a series of metal tubes or channels that guide the microwaves with minimal loss of energy. The design and efficiency of the waveguide system play a crucial role in ensuring uniform heating throughout the product.
3. Drying Chamber:
The drying chamber is where the actual drying process takes place. It is typically a sealed enclosure that contains the product being dried. The walls of the drying chamber are constructed from materials that are transparent to microwave radiation, allowing the waves to penetrate and heat the product evenly.
4. Control System:
The control system of the microwave dryer machine governs the operation of the equipment. It includes a user interface for setting parameters such as drying time, temperature, and power level. Additionally, advanced models may incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to monitor and adjust the drying process in real-time for optimal results.
5. Cooling System:
Given the high temperatures generated during the drying process, a cooling system is essential to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation of the equipment. This system may consist of fans, heat exchangers, or other cooling mechanisms designed to dissipate excess heat and maintain the desired temperature within the drying chamber.
Comparison and advantages of microwave technology and traditional drying methods
Aspect | Microwave Dryer Machine | Traditional Drying Methods |
Drying Time | Significantly faster drying times | Longer drying times |
Energy Efficiency | Higher energy efficiency | Lower energy efficiency |
Product Quality | Preserves product quality | May result in degradation |
Temperature Control | Precise temperature control | Limited control over temperature |
Uniformity of Drying | Provides more uniform drying | May result in uneven drying |
Space Requirement | Compact design, requires less space | Requires more space |
Labor Intensity | Requires less manual labor | May require more manual labor |
Environmental Impact | Lower environmental impact | Higher environmental impact |
This table succinctly illustrates the key advantages of microwave dryer machines over traditional drying methods in 2024, including faster drying times, higher energy efficiency, superior product quality, precise temperature control, uniform drying, compact design, reduced labor intensity, and lower environmental impact.
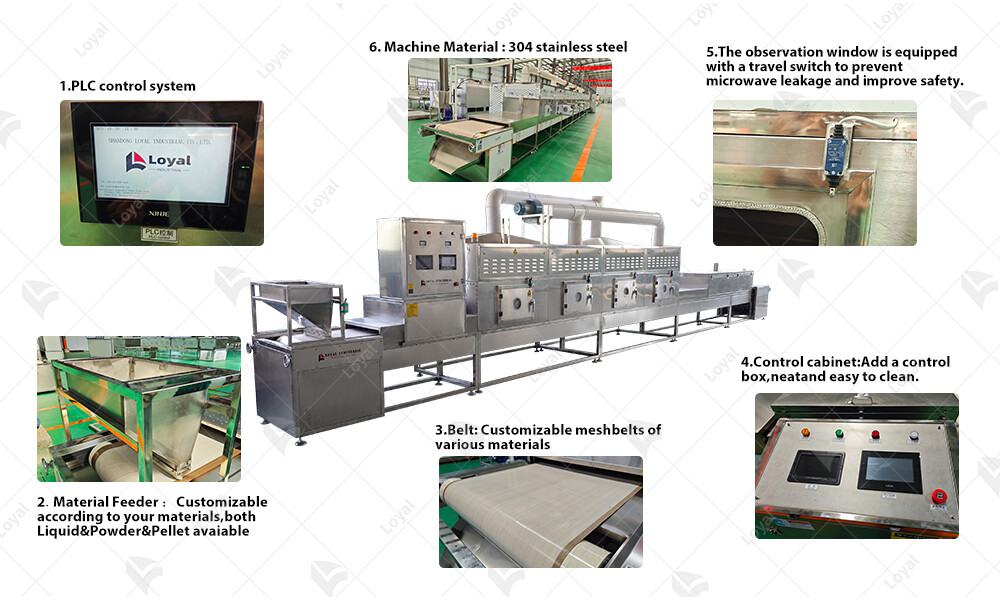

Technical parameters
| Technical Parameters Of Continuous Microwave Dryer Industrial Microwave Drying Machine | |||||
| Model | Size LWH(Can be customized according to the customer's requirements) | Output power | Dewaterability | Sterilization capacity | Baking and Roasting capacity (Depends on different raw material) |
| LY-10KW | 5000mm825mm1750mm | ≥10KW | 10KG/Hour | 100KG/Hour | 30-50KG/Hour |
| LY-20KW | 8000mm825mm1750mm | ≥20KW | 20KG/Hour | 200KG/Hour | 60-100KG/Hour |
| LY-30KW | 8500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥30KW | 30KG/Hour | 300KG/Hour | 90-150 KG/Hour |
| LY-40KW | 10000mm1160mm1750mm | ≥40KW | 40KG/Hour | 40KG/Hour | 120-200KG/Hour |
| LY-50KW | 12500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥50KW | 50KG/Hour | 500KG/Hour | 150-250KG/Hour |
| LY-60KW | 13500mm1450mm1750mm | ≥60KW | 60KG/Hour | 600KG/Hour | 180-300KG/Hour |
| LY-70KW | 13500mm1500mm1750mm | ≥70KW | 70KG/Hour | 700KG/Hour | 210-350KG/Hour |
| LY-80KW | 13500mm1650mm1750mm | ≥80KW | 80KG/Hour | 800KG/Hour | 240-400KG/Hour |
| LY-100KW | 16800mm1650mm1750mm | ≥100KW | 100KG/Hour | 1000KG/Hour | 300-500KG/Hour |
| LY-150KW | 22400mm1850mm1750mm | ≥150KW | 150KG/Hour | 1500KG/Hour | 450-750KG/Hour |
| LY-200KW | 27000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥250KW | 250KG/Hour | 2500KG/Hour | 750-1250/Hour |
| LY-300KW | 32000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥300KW | 300KG/Hour | 3000KG/Hour | 900-1500KG/Hour |
| Power Supply | 380V±10% 50Hz±1% Three-Phase Five-Wire | ||||
| Microwave Output Frequency | 2450±50Mhz | ||||
| Microwave Input Apparent Power | ≤168Kva | ||||
| Microwave Output Power | ≥120Kw | ||||
| Microwave Power Adjustment Range | 0-30Kw(Adjustable) | ||||
| Ambient Temperature | -5-40°C | ||||
| Relative Humidity | ≤80%, Surrounding Environment:No Corrosive Gas, Conductive Dust And Explosive Gas | ||||
| Transmission Speed | 0-10m/Min(Adjustable) | ||||
Technological Progress and Innovation of Microwave Dryer Machines
1. Advanced Heating Mechanisms:
Microwave dryer machines utilize electromagnetic waves to generate heat within the product, unlike conventional dryers that rely on external heating elements. This direct heating mechanism results in faster and more uniform drying, reducing processing times and preserving the nutritional integrity of the food.
2. Integration of Automation and IoT:
Modern microwave dryer machines are equipped with advanced automation features and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity. These technologies enable remote monitoring and control of the drying process, allowing operators to adjust parameters in real-time for optimal performance. Additionally, predictive maintenance algorithms anticipate potential issues, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
3. Precise Temperature and Moisture Control:
One of the key innovations in microwave dryer machines is the ability to precisely control temperature and moisture levels throughout the drying process. This ensures consistent results and minimizes the risk of over-drying or under-drying, leading to superior product quality and extended shelf life.
4. Energy-Efficient Design:
Efficiency and sustainability are paramount considerations in the design of modern microwave dryer machines. Advanced insulation materials and energy-saving components minimize heat loss and reduce overall energy consumption. Additionally, innovative heat recovery systems capture and reuse waste heat, further enhancing efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
5. Customizable Configurations:
Manufacturers offer a range of customizable configurations to suit diverse applications and processing requirements. From batch dryers for small-scale operations to continuous conveyor systems for large-scale production, microwave dryer machines can be tailored to meet specific needs while maintaining efficiency and reliability.
6. Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms enables microwave dryer machines to continuously optimize performance based on real-time data and feedback. Machine learning algorithms analyze various factors, including product characteristics, ambient conditions, and processing parameters, to dynamically adjust settings and maximize efficiency.

Challenges and limitations of microwave dryers
1. Uneven Heating:
One of the primary challenges associated with microwave dryer machines is the issue of uneven heating. Due to the nature of microwave energy, there can be inconsistencies in the distribution of heat within the product, leading to uneven drying. This uneven heating may result in variations in product quality and texture, posing a challenge for manufacturers striving for uniformity.
2. Limited Penetration Depth:
Microwave energy tends to penetrate only a few centimeters into the surface of the product, limiting its effectiveness in drying thick or dense materials. This limitation can lead to incomplete drying or longer processing times for certain products, affecting overall efficiency and productivity.
3. Product Sensitivity:
Certain food products, particularly those with high moisture content or varying densities, may react differently to microwave drying. Some products may be more susceptible to overheating or uneven drying, requiring careful adjustment of process parameters to achieve optimal results. This sensitivity adds complexity to the drying process and may necessitate specialized equipment or techniques for certain applications.
4. Energy Consumption:
While microwave drying is generally more energy-efficient than conventional drying methods, it still requires significant power to operate. High-power microwave generators and complex control systems contribute to energy consumption, leading to increased operating costs, particularly for large-scale industrial applications. Manufacturers must carefully consider the balance between the benefits of rapid drying and the associated energy costs.
5. Equipment Maintenance and Safety:
Maintaining and operating microwave dryer machines requires specialized training and expertise. High-power microwave radiation poses safety risks to operators, necessitating strict adherence to safety protocols and regulations. Additionally, the complex nature of microwave drying equipment requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and safety, adding to the overall operational costs.
In conclusion, while microwave dryer machines offer numerous benefits in terms of efficiency and quality, they are not without their challenges and limitations. Manufacturers must address these challenges through innovation and careful optimization of process parameters to fully realize the potential of microwave drying technology in 2024 and beyond.
Post-Maintenance of Microwave Dryer Machine
After the initial installation and setup of microwave dryer machines, proper post-maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Microwave dryer machines are intricate pieces of equipment that require regular upkeep to operate efficiently. In this section, we will outline key post-maintenance practices for microwave dryer machines in 2024.
1. Routine Cleaning:
Regular cleaning is crucial for maintaining the hygiene and efficiency of microwave dryer machines. After each use, remove any food residues, spills, or debris from the interior and exterior surfaces of the machine. Use mild detergent and warm water to clean the interior chamber, ensuring thorough removal of any contaminants.
2. Inspection of Components:
Periodically inspect all components of the microwave dryer machine for signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Check the door seals, hinges, and latches for tightness and proper functioning. Examine the heating elements, fans, and electronic controls for any abnormalities or irregularities in operation.
3. Calibration and Adjustment:
Regular calibration and adjustment of microwave power levels and timing settings are essential to maintain consistent drying performance. Use calibrated thermometers and moisture meters to verify the accuracy of temperature and moisture levels within the drying chamber. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure uniform drying across all batches.
4. Lubrication of Moving Parts:
Ensure proper lubrication of moving parts such as fan motors, conveyor belts, and bearings to reduce friction and prevent premature wear. Use lubricants recommended by the manufacturer and follow the specified lubrication schedule. Inspect lubrication points regularly and replenish lubricants as needed.
5. Safety Checks:
Conduct regular safety checks to identify and address any potential hazards or safety concerns. Inspect electrical connections, cords, and plugs for signs of damage or wear. Test emergency stop buttons, overload protection devices, and interlock systems to ensure they are functioning correctly. Address any safety issues promptly to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries.
6. Documentation and Record-Keeping:
Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities performed on the microwave dryer machine. Keep track of cleaning schedules, inspections, repairs, and calibration procedures. Document any issues or abnormalities encountered during maintenance and record the actions taken to address them. This documentation will serve as a valuable reference for future maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
By following these post-maintenance practices diligently, operators can ensure the reliability, efficiency, and safety of microwave dryer machines in 2024 and beyond. Regular maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also ensures consistent drying performance and product quality, contributing to overall operational success in the food processing industry.

References
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites in the field of industrial microwaves:
1. IEEE Xplore Digital Library
Website: [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/]
2.ScienceDirect
Website: [https://www.sciencedirect.com/]
3. SpringerLink
Website: [https://link.springer.com/]
4. Wiley Online Library
Website: [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/]
5. PubMed
Website: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/]