Exploring the Four Safe Methods for Thawing Frozen Food
Thawing frozen food is a critical process in the food service industry, impacting both the quality and safety of the food served. The method chosen for thawing can significantly affect the texture, flavor, and nutritional value of food, making it imperative to select the right technique for specific food types. Additionally, improper thawing can lead to foodborne illnesses due to the growth of harmful bacteria if the food remains at unsafe temperatures for too long.
To address these challenges, industrial defrosting equipment plays a pivotal role in large-scale food operations. This equipment is designed to thaw large quantities of food quickly and uniformly, ensuring that all parts of the food reach appropriate temperatures to inhibit bacterial growth while maintaining product integrity. Dr. Susan Blumenthal, a food safety expert, notes, "Using advanced defrosting technologies not only enhances food safety but also preserves the quality, which is crucial in food handling and processing industries."
By integrating industrial defrosting equipment into their operations, businesses can achieve more efficient thawing processes, which is essential for maintaining high standards of food quality and safety in today’s fast-paced culinary environments.
Method 1: Refrigerator Thawing
One of the safest and most recommended methods for thawing frozen food is using a refrigerator. This method involves placing frozen food in the refrigerator and allowing it to thaw slowly, usually over several hours or overnight, depending on the size and type of food. This slow thawing process helps ensure that food remains at a safe temperature (below 40°F or 4°C), which minimizes the risk of bacterial growth.
Advantages of Refrigerator Thawing
- Safety: Keeping food at a consistent, safe temperature reduces the risk of harmful bacteria proliferation.
- Quality Preservation: The gentle thawing process helps maintain the food’s texture, flavor, and nutritional value, making it ideal for meats, poultry, and delicate items like seafood.
- Convenience: Once thawed, the food can safely remain in the refrigerator for a day or two before cooking, providing flexibility in meal preparation.
Timeline Considerations
- Small items such as breasts of chicken or a couple of pounds of ground meat can typically thaw within a day.
- Larger items like whole turkeys or large roasts may require up to 24 hours for every 5 pounds of weight.
Chef Anthony Gomes, a professional chef with over 20 years of experience in gourmet restaurants, advocates for this method, stating, “Refrigerator thawing, though slower, allows for optimal control over the thawing process, ensuring that the food’s quality and safety are not compromised. It’s especially crucial for high-quality ingredients used in professional kitchens.”
By utilizing refrigerator thawing, food service operations can ensure that they are not only serving safe food but also maximizing the sensory qualities of their meals, aligning with high culinary standards.
Method 2: Cold Water Thawing
Cold water thawing is a faster alternative to refrigerator thawing, suitable for situations where time is a constraint. This method involves submerging the frozen food in cold water, ensuring the packaging is airtight and water-resistant to prevent water from absorbing into the food.
Steps for Thawing Food Using the Cold Water Method
- Ensure Packaging Integrity: Check that the food is in a leak-proof package. This prevents water from contacting the food, which can alter texture and increase the risk of bacterial contamination.
- Submerge in Cold Water: Place the food in a large bowl or sink and completely submerge it in cold water. Change the water every 30 minutes to ensure it remains cold.
- Monitor Thawing Process: Small items may thaw in as little as an hour, while larger items could take 2-3 hours.
Safety Tips
- Keep Water Cold: It's essential to use cold water and change it regularly to maintain a safe temperature throughout the thawing process.
- Cook Immediately After Thawing: To minimize the risk of bacterial growth, cook the food immediately after it has thawed completely.
Efficiency of This Method
Cold water thawing is significantly faster than refrigerator thawing, making it a practical choice for quick meal preparation. It is particularly effective for smaller food items that need to be cooked promptly.
Dr. Lisa Hamilton, a food safety specialist, emphasizes, "While cold water thawing can be done more quickly than refrigerator thawing, it requires more attention to ensure safety. Regularly changing the water and maintaining low temperatures are critical to preventing bacterial growth."
This method is a useful technique for food service operations that need to prepare meals quickly but still prioritize food safety. Its effectiveness and relative speed make it an excellent choice for thawing meat, poultry, and seafood when time constraints are tight.
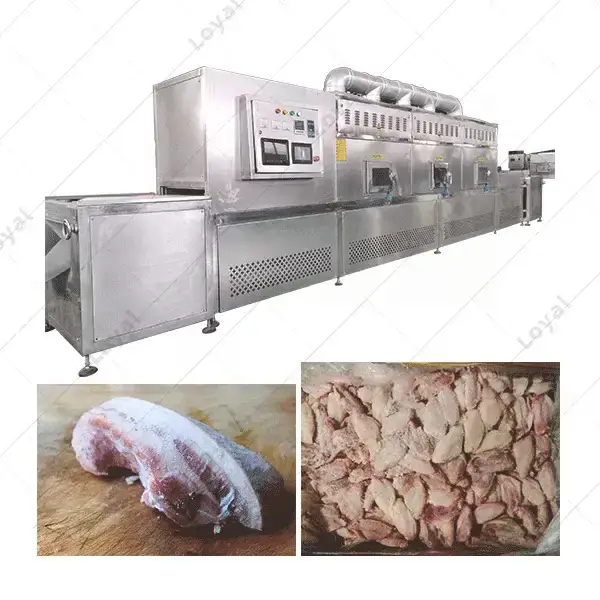
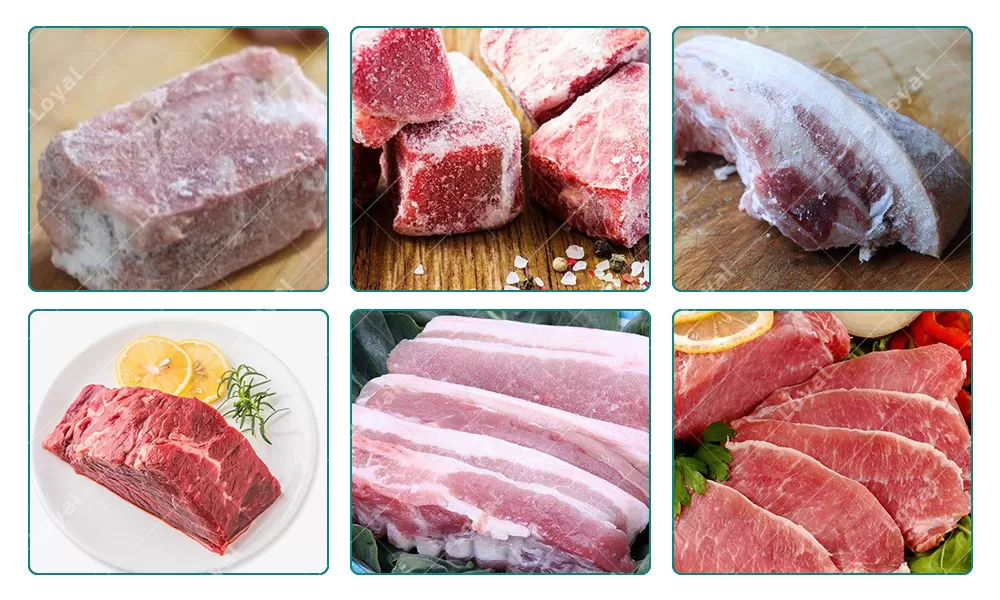


Method 3: Microwave Thawing
Microwave thawing is the fastest method for defrosting frozen food, making it ideal for last-minute meal preparations. This method utilizes the microwave's defrost setting to quickly reduce ice crystals in food without cooking it.
Guidelines for Using a Microwave to Thaw Food Safely
- Use the Defrost Setting: Most microwaves come with a defrost setting that lowers the appliance's power to avoid cooking the food while defrosting.
- Size and Shape Consideration: Arrange the food evenly in the microwave-safe dish, and if possible, separate pieces to allow uniform thawing.
- Rotate and Flip: Rotate and flip the food periodically during the defrosting process to ensure even thawing.
Importance of Cooking Immediately After Microwave Thawing
- Prevent Bacterial Growth: Because some areas of the food may begin to cook during microwave thawing, it’s critical to cook it immediately after thawing to prevent any bacteria that might have multiplied from surviving.
- Quality Preservation: Immediate cooking helps preserve the food's texture and flavor, which microwave thawing can sometimes compromise.
Potential Drawbacks
- Uneven Thawing: Microwaves can thaw food unevenly, which is a particular concern for larger or denser food items.
- Texture Changes: Some foods may partially cook during the thawing process, which could affect their final texture and taste.
Chef Julie Chen, an expert in culinary techniques, advises, “Microwave thawing should be used sparingly and primarily for small or thin pieces of food. It’s a practical method when in a rush, but it requires vigilance to ensure food is evenly thawed and immediately moved to cooking.”
Microwave thawing is a practical method for those who need to prepare food quickly. However, it demands careful handling to ensure that the rapid temperature changes do not compromise food safety or quality.
Method 4: Thawing with Industrial Defrosting Equipment
For large-scale food service operations, using industrial defrosting equipment can significantly enhance the efficiency and uniformity of thawing large quantities of frozen food. This method leverages advanced technology to ensure that the thawing process meets high standards of speed and safety.
Explanation of How Industrial Defrosting Equipment Works
Industrial defrosting equipment typically uses methods such as:
- Conductive Heat Transfer: Directly heats containers holding the frozen food.
- Microwave or Radio Frequency Defrosting: Uses electromagnetic waves to quickly thaw food by generating heat internally.
- Air Blast Defrosting: Circulates warm air over and around the food to gradually increase its temperature.
Benefits of Using Industrial Methods
- Speed: Industrial defrosting can thaw large batches of food much faster than manual methods.
- Uniformity: These systems are designed to thaw food evenly, reducing the risk of some parts remaining frozen while others begin to cook.
- Scalability: Suitable for operations that need to process large amounts of food, ensuring consistency across all items.
Types of Industrial Defrosting Equipment and Their Applications
- Microwave Thawing Units: Best for rapid thawing of meats and seafood that can be quickly processed further.
- Infrared Thawing Systems: Efficient for surface thawing of large items.
- Cryogenic Thawing: Uses controlled exposure to very low temperatures and is ideal for sensitive or high-value food products.
Dr. Alberto Gomez, a specialist in food processing technology, highlights the advantages: “Industrial defrosting equipment is transformative for food processing industries. It not only optimizes the thawing process but also integrates seamlessly into existing production lines to increase throughput and maintain product integrity.”
For commercial settings where time and consistency are critical, investing in industrial defrosting equipment can dramatically improve operational efficiency and food quality. This method is especially beneficial in settings where precise temperature control and handling large volumes are routine.

Best Practices for Handling Thawed Food
Once food has been thawed, especially in a commercial setting, handling it correctly is crucial to maintaining food safety and quality. Here are some essential tips to ensure that thawed food is handled safely:
Tips on How to Handle Food Once It Has Been Thawed
- Maintain Temperature Control: Keep thawed food at safe temperatures. Foods should not be left at room temperature for more than two hours to prevent bacterial growth.
- Segregate Thawed Food: Store thawed food separately from other foods, particularly raw foods, to avoid cross-contamination.
- Use Quickly: Plan to use thawed food within 24-48 hours to ensure it remains fresh and safe to eat.
Importance of Cooking Thawed Food to the Right Temperatures
- Ensure Thorough Cooking: Cooking thawed food to the recommended internal temperatures is critical to destroy any harmful bacteria that may have developed during the thawing process. For example, poultry should be cooked to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C), and beef to at least 145°F (63°C) with a rest time.
- Use a Food Thermometer: Always use a food thermometer to check the internal temperature of cooked foods to ensure they are safe to eat.
Storage Advice for Thawed Food if Not Used Immediately
- Refrigeration: If not used immediately, keep thawed food in the refrigerator and plan to use it within the recommended time frame.
- Re-freezing: Generally, it is safe to refreeze thawed food that has been handled properly and kept chilled. However, there might be a loss of quality due to moisture loss during thawing.
Dr. Emily Carlton, a food safety expert, stresses the importance of these practices: "Proper handling and cooking of thawed food are paramount in any food service operation. Adhering to these practices not only ensures safety but also helps in maintaining the nutritional and sensory qualities of the food."
Following these best practices for handling thawed food can help food service operations manage food safety risks effectively and ensure that meals served are of the highest quality and safety.
Conclusion
Exploring the four safe methods for thawing frozen food highlights the importance of choosing the right technique based on your specific needs, especially in commercial food service operations. Whether using the slow and steady refrigerator thawing, the quicker cold water method, the rapid microwave technique, or employing advanced industrial defrosting equipment, each method offers unique benefits and is suited to different operational demands and food types.
Implementing these methods effectively requires understanding their advantages, limitations, and best practices, as discussed. Moreover, maintaining rigorous standards in handling thawed food—by ensuring it is cooked to proper temperatures and stored safely—further ensures the quality and safety of the meals served.
For commercial operations, investing in industrial defrosting equipment can be particularly beneficial, providing speed, efficiency, and uniformity in thawing large volumes of food. Such equipment not only supports compliance with food safety regulations but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
In conclusion, the method of thawing food should be chosen with care, consideration, and knowledge of how each impacts food safety and quality. Regularly reviewing and optimizing these methods according to the latest industry standards and technological advances will help maintain the highest levels of food safety and customer satisfaction in any culinary establishment.