Exploring the Process of Pasta Production within a Factory Setting
The journey of pasta from a simple mixture of flour and water to a global culinary staple is a fascinating tale of innovation, tradition, and technological advancement. The pasta production industry plays a crucial role in the global food market, supplying millions of households with this versatile and beloved food item. The origins of pasta manufacturing trace back to ancient times, but it was the introduction of modern production techniques that transformed pasta into a staple of convenience and nutritional value.
The evolution of pasta manufacturing has been marked by significant milestones, from the manual crafting of noodles to the advent of mechanization in the 19th century. The development of the macaroni making machine was a game-changer, revolutionizing the industry by drastically increasing production capabilities and standardizing the quality of the pasta produced.
Today, modern pasta factories are marvels of technological sophistication, employing advanced automation to ensure high efficiency and consistency in pasta production. Automation plays a pivotal role in the entire production process, from mixing ingredients to packaging the final product. According to food industry expert Dr. Angela Rossi, "The automation of pasta production has not only optimized manufacturing processes but also significantly enhanced the ability to meet the growing global demand for pasta."
This introduction to pasta production within a factory setting highlights the remarkable journey of pasta manufacturing. It underscores the importance of innovation and technological advancement in meeting the needs of consumers worldwide. The macaroni making machine stands out as a cornerstone of modern pasta factories, symbolizing the blend of tradition and technology that characterizes the pasta production industry.

Key Ingredients and Preparation
The foundation of any pasta, including those produced on an industrial scale, lies in its simple yet fundamental ingredients: semolina and water, with eggs often added for certain varieties. These ingredients, when combined, form the dough that is the basis for a myriad of pasta shapes and types, each beloved in different culinary traditions around the world.
Semolina: The Core of Pasta Dough
Semolina, derived from durum wheat, is the cornerstone ingredient for pasta production. Its high gluten content and coarse texture make it ideal for creating pasta with the perfect balance of elasticity, firmness, and ability to hold shape during cooking. The quality of semolina is a critical factor in the production process, influencing not only the taste and texture of the pasta but also its nutritional value.
Water: The Binding Element
Water acts as the catalyst in transforming semolina into dough. The quantity and temperature of water added play a crucial role in determining the dough's consistency and workability. In industrial settings, precise measurements and controls ensure that the dough maintains a uniform standard across batches, essential for the automated machinery, such as the macaroni making machine, to function optimally.
Eggs: For Specialty Pasta
In some pasta varieties, eggs are introduced into the dough mixture to enhance flavor, nutritional content, and texture. Egg pasta is especially popular in certain regional cuisines and offers a richer taste and a more tender bite. The inclusion of eggs, while not universal, demonstrates the versatility of pasta production and the adaptability of the manufacturing process to cater to diverse culinary preferences.
The Mixing and Kneading Process
The mixing and kneading of the ingredients are where the magic begins. Industrial mixers combine semolina, water, and possibly eggs under controlled conditions to ensure a homogenous mixture. The kneading process then develops the gluten network within the dough, providing the necessary structure and elasticity. This step is crucial for the pasta's ability to withstand the pressures of extrusion and cooking without losing its integrity.
The preparation of the dough is a testament to the blend of art and science that defines pasta production. As noted by culinary scientist Dr. Lorenzo Bianchi, "The precision in dough preparation is what sets the foundation for high-quality pasta. From the humidity of the water to the protein content of the semolina, every detail matters in achieving the perfect dough consistency."
This careful preparation of ingredients and dough is essential for the subsequent stages of pasta production, especially as the dough moves on to be shaped and cut by the macaroni making machine. It is this attention to detail and commitment to quality at every step that ensures the final product meets the high standards expected by consumers around the globe.
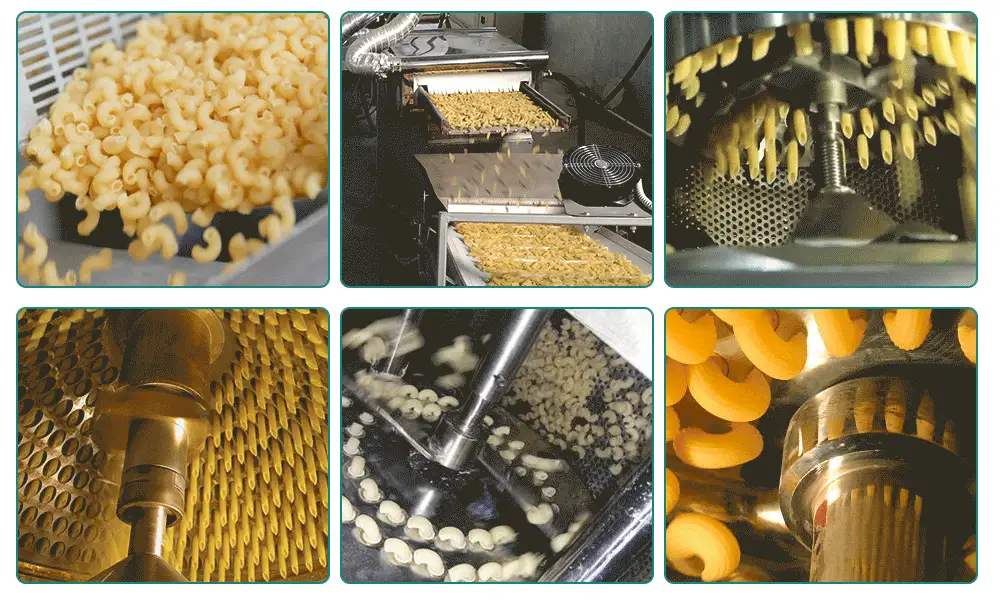
The Role of the Macaroni Making Machine
In the orchestrated symphony of pasta production, the macaroni making machine plays a leading role, transforming meticulously prepared dough into the myriad shapes and sizes of pasta adored worldwide. This equipment, emblematic of modern pasta manufacturing, encapsulates the fusion of tradition and technology, streamlining the production process while maintaining the quality and authenticity of the pasta produced.
Core Functions of the Macaroni Making Machine
The macaroni making machine operates by extruding pasta dough through molds or dies to form various shapes, from the classic tube of macaroni to intricate designs like fusilli or rotini. The extrusion process is critical, as it determines the texture and surface of the pasta, which in turn affects how the pasta holds sauce and cooks. Advanced machines are equipped with customizable settings, allowing for precise control over size, shape, and texture, ensuring consistency across production batches.
Versatility in Pasta Production
One of the machine’s standout features is its versatility. By simply changing the extrusion dies, manufacturers can switch between pasta types quickly and efficiently, meeting diverse consumer preferences without the need for extensive downtime or equipment changes. This adaptability makes the macaroni making machine a valuable asset in any pasta production line, enabling producers to respond to market trends and demands with agility.
Enhancing Production Efficiency
The integration of a macaroni making machine into the production line markedly enhances efficiency. These machines are designed for high-volume production, capable of producing vast quantities of pasta within short time frames. Their automation reduces labor costs and minimizes human error, ensuring that each piece of pasta is extruded to perfection. Furthermore, the continuous operation of these machines meets the high demands of the global food market, supplying consumers with a constant and consistent product.
Quality Assurance
Beyond shaping pasta, the macaroni making machine also plays a crucial role in quality assurance. Modern machines are often equipped with sensors and monitoring systems to detect any deviations in dough consistency or extrusion parameters, allowing for real-time adjustments. This capability ensures that the pasta not only meets the manufacturer's standards but also complies with food safety regulations.
Renowned food processing engineer, Dr. Marco Ferrari, highlights the significance of these machines, stating, "The macaroni making machine has revolutionized pasta production, combining the art of pasta making with the precision and efficiency of modern technology. It’s a testament to how innovation can preserve tradition while propelling it into the future."
As such, the macaroni making machine is more than just a piece of equipment; it is the heart of the pasta production process, embodying the evolution of an age-old culinary art into a modern industrial achievement. Its role in the factory setting is indispensable, marrying tradition with technology to produce pasta that is loved globally.
Drying and Quality Control
Following the transformative journey of dough through the macaroni making machine, the next critical phases in pasta production are drying and quality control. These stages are paramount, not only for ensuring the pasta’s shelf stability and texture but also for maintaining the high quality that consumers expect.
The Drying Process
Drying is a delicate balance; it must remove enough moisture to prevent spoilage, yet retain enough to ensure the pasta doesn’t become too brittle. Modern pasta factories utilize precise drying techniques, often involving controlled temperature and humidity levels over extended periods. This methodical approach ensures that the pasta dries uniformly, preventing issues such as cracking or warping. The drying phase can vary significantly depending on the pasta shape and size, with complex shapes or thicker pasta requiring more time.
Technology in Drying
Advancements in drying technology have significantly improved efficiency and consistency in pasta production. Programmable drying chambers allow for the fine-tuning of conditions, accommodating different types of pasta with customized drying cycles. These technological advancements enable manufacturers to achieve the ideal texture and firmness, crucial for cooking performance.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is an ongoing process throughout pasta production, becoming especially rigorous post-drying. This stage includes both visual inspections and laboratory testing to assess the pasta's appearance, texture, and nutritional content. Modern factories often employ automated systems equipped with cameras and sensors to detect any defects, such as irregular shapes or sizes, ensuring only the highest quality products proceed to packaging.
Furthermore, samples from each batch are frequently tested for moisture content, ensuring they fall within the optimal range for shelf stability. Additional tests may include checking for microbial contamination and verifying the nutritional content aligns with labeling.
Ensuring Food Safety and Compliance
Quality control also encompasses adherence to food safety standards and regulatory compliance. Factories implement Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plans to identify potential hazards and establish critical control points in the production process. These measures are vital for preventing contamination and ensuring the pasta is safe for consumption.
Renowned food safety expert, Dr. Emily Chen, underscores the importance of these protocols, stating, "Quality control and food safety measures in pasta production are not merely regulatory obligations but are fundamental to consumer trust and brand integrity. Through meticulous quality assurance practices, manufacturers can guarantee a product that is not only delicious but safe."
Drying and quality control are thus integral to the pasta production process, ensuring that the pasta not only meets the aesthetic and culinary standards expected by consumers but also adheres to the highest safety and quality standards. The evolution of drying technologies and quality control methods continues to elevate the standards of pasta production, reflecting the industry's commitment to excellence and consumer satisfaction.
Packaging and Distribution
After the meticulous processes of extrusion, drying, and quality control, the pasta is ready for the final stages of packaging and distribution. These steps are crucial for preserving the quality of the pasta, ensuring it reaches consumers in optimal condition, and facilitating the product's journey from the factory to dinner tables around the world.
Packaging: The First Line of Defense
Packaging serves multiple critical functions: it protects the pasta from physical damage, contamination, and moisture – all of which could compromise the product's quality and shelf life. Modern pasta factories employ automated packaging lines that weigh, fill, and seal packages at high speeds, ensuring efficiency and accuracy. The choice of packaging materials, from traditional plastic to more sustainable options, is carefully considered to balance product protection, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
Innovative packaging solutions, such as modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), are increasingly used to extend shelf life further without the need for preservatives. This technology adjusts the composition of the air within the package, slowing down oxidation and the growth of spoilage organisms.
Distribution: Navigating the Global Supply Chain
Once packaged, the pasta is ready for distribution, a complex logistical operation given the global nature of the food market. Manufacturers must navigate a web of retailers, distributors, and logistics providers to ensure their products reach a wide array of markets efficiently. The distribution process is carefully planned to minimize transit times and protect the pasta from temperature extremes, humidity, and rough handling, which could affect its quality.
Strategic distribution centers play a vital role in this process, acting as hubs from which pasta can be swiftly dispatched to various destinations. The use of advanced inventory and logistics management software allows manufacturers to track shipments in real-time, optimize delivery routes, and manage stock levels effectively, reducing waste and ensuring freshness.
Meeting Consumer Demand Across the Globe
The global pasta market is diverse, with regional preferences for different pasta shapes, sizes, and types. Manufacturers must consider these preferences in both product offerings and distribution strategies. For instance, a pasta shape popular in one region may not be in another, necessitating targeted distribution strategies to match local market demands.
As highlighted by logistics expert Dr. Marco Silva, "The global distribution of pasta requires a nuanced understanding of both the product and the markets it serves. Manufacturers must leverage sophisticated logistics solutions to meet the diverse needs of consumers worldwide, ensuring that every package of pasta delivers not just food, but an experience."
Packaging and distribution are the final, critical steps in bringing pasta from the factory to consumers, ensuring that the care and precision applied throughout the production process result in a high-quality product enjoyed by people everywhere. As the pasta industry continues to evolve, so too will the techniques and technologies used in these stages, driven by the twin goals of quality preservation and environmental sustainability.
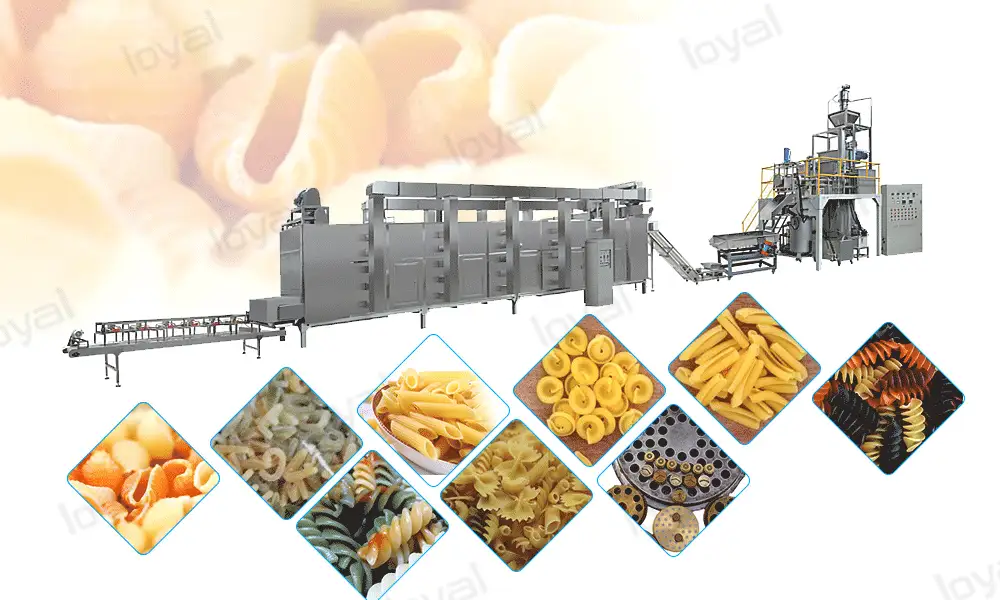

Conclusion
The intricate journey of pasta production, from the initial mixing of simple ingredients to the final steps of packaging and global distribution, showcases a remarkable blend of tradition and technological innovation. The macaroni making machine stands as a testament to this synthesis, representing the heart of the modern pasta production line and playing a pivotal role in transforming raw ingredients into the diverse shapes and flavors of pasta that grace dining tables worldwide.
Throughout each phase of production—ingredient preparation, dough extrusion, drying, quality control, packaging, and distribution—precision and care are paramount. The adoption of advanced technologies and meticulous quality assurance practices ensure that the final product not only meets but exceeds consumer expectations in terms of taste, texture, and nutritional value.
The global pasta market continues to thrive, driven by consumers' enduring love for this versatile and comforting food. As manufacturers navigate the complexities of production and distribution, they are also responding to evolving consumer preferences with innovations in pasta types, ingredients, and sustainable practices.
Reflecting on the process of pasta production within a factory setting, it is clear that the macaroni making machine and subsequent technologies have not only streamlined manufacturing but have also preserved the essence of pasta that has been cherished for centuries. As Dr. Angela Rossi aptly noted, "The future of pasta production lies in balancing efficiency with sustainability, ensuring that we continue to enjoy this staple food in a way that respects both our heritage and our planet."
In conclusion, exploring the process of pasta production reveals much about our capabilities to innovate and adapt, ensuring that this simple yet beloved food continues to enrich our lives. The journey from flour to fork encapsulates a story of cultural significance, technological advancement, and collective enjoyment—a story that continues to unfold with every plate of pasta served.