Everything you need to know about corn flakes maker machine in 2024
Overview of the Cereal Processing Industry
The cereal processing industry is a cornerstone of the global food market, supplying millions of consumers with their daily breakfast staples. From cornflakes to granola, the variety of cereals available today is a testament to the industry's evolution and innovation. Traditionally, cereal production involved multiple stages of manual intervention, which not only prolonged the manufacturing process but also increased the risk of inconsistencies in product quality.
Importance of Innovation in Breakfast Production
In an era where efficiency and quality are paramount, the need for innovation in breakfast production has never been more critical. Consumers demand not only a diverse range of cereal products but also consistent quality and nutritional value. As such, manufacturers are under constant pressure to enhance their production capabilities while maintaining stringent quality standards. This is where the concept of a fully automatic cereal processing line comes into play, offering a revolutionary approach to breakfast production.
Brief Introduction to the Concept of a Fully Automatic Cereal Processing Line
A fully automatic cereal processing line represents a significant leap forward in food machinery technology. Unlike traditional processing lines, which rely heavily on manual labor and segmented machinery, fully automatic lines integrate advanced automation technologies to streamline the entire production process. From raw material handling to packaging, these systems are designed to operate with minimal human intervention, thereby reducing labor costs, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring consistent product quality.
The integration of automation in cereal processing lines encompasses a range of sophisticated technologies, including robotics, smart sensors, and real-time data analytics. These components work in harmony to optimize every stage of production, from mixing and cooking to shaping and drying. As a result, manufacturers can achieve higher output rates, reduce waste, and improve overall operational efficiency.
In the subsequent sections of this article, we will delve deeper into the components and benefits of fully automatic cereal processing lines, explore key technologies driving these innovations, and examine case studies of successful implementations. We will also address the challenges and considerations associated with adopting these advanced systems and provide insights into the future of cereal processing lines in the breakfast cereal market.
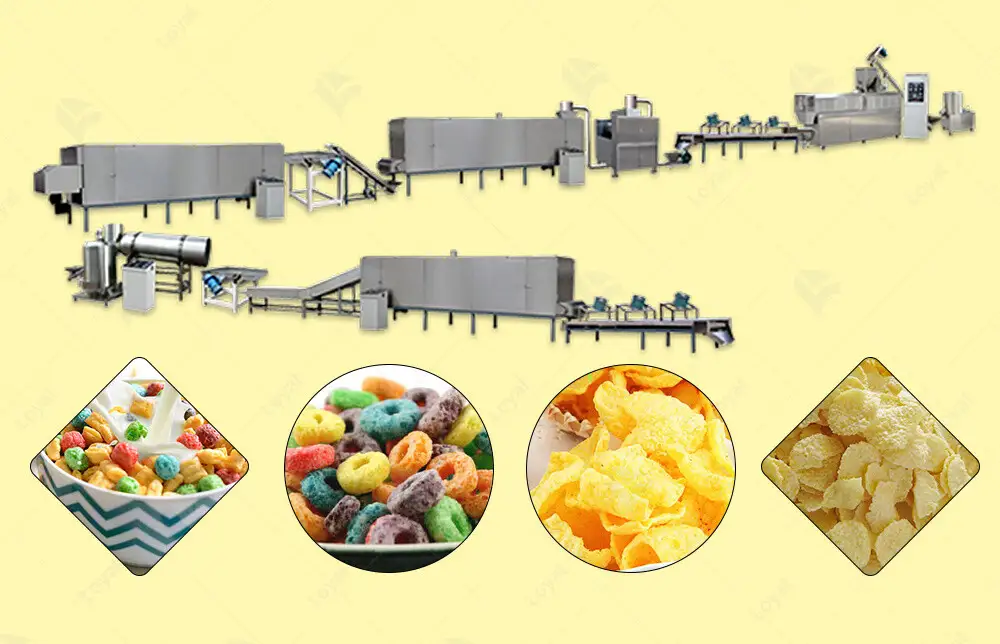

What is a Fully Automatic Cereal Processing Line?
Definition and Key Components
A fully automatic cereal processing line is an advanced system designed to handle the entire cereal production process with minimal human intervention. This type of system integrates various technologies to perform a series of operations, including cleaning, sorting, cooking, shaping, drying, and packaging of cereals. Key components of a fully automatic cereal processing line include:
*Cleaning and Sorting Machines:** These machines remove impurities and sort grains based on size and quality.
*Cooking Equipment:** This includes extruders and ovens that cook the grains to the desired texture and taste.
*Shaping Machines:** These machines mold the cooked grains into specific shapes, such as flakes, puffs, or rings.
*Drying Equipment:** This equipment ensures the cereals are dried to the right moisture content, enhancing shelf life and texture.
*Packaging Machines:** These machines package the final product into various formats, such as boxes, bags, or pouches, ready for distribution.
How It Differs from Traditional Processing Lines
Traditional cereal processing lines rely heavily on manual labor and multiple discrete machines for different stages of production. These lines often involve significant manual intervention for monitoring, adjusting, and transferring products between stages. In contrast, a fully automatic cereal processing line integrates all these stages into a seamless, automated process. Automation ensures precise control over each step, reduces human error, and significantly enhances production speed and consistency.
The Role of Automation in Modern Food Production
Automation plays a crucial role in modern food production by increasing efficiency, ensuring product quality, and reducing operational costs. In the context of cereal processing lines, automation involves the use of advanced machinery and smart technologies to monitor and control the entire production process. This includes real-time data collection and analysis, which helps in making informed decisions and optimizing the production line for maximum efficiency.
By automating the cereal processing line, manufacturers can achieve consistent product quality, adhere to strict hygiene standards, and minimize wastage. Moreover, automation allows for greater flexibility in production, enabling manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing market demands and produce a wider variety of cereal products. As a result, the adoption of fully automatic cereal processing lines is becoming increasingly essential for staying competitive in the food manufacturing industry.

Benefits of Fully Automatic Cereal Processing Lines
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
| One of the most significant benefits of a fully automatic cereal processing line is the substantial increase in efficiency and productivity. Automation streamlines the entire production process, from the initial cleaning and sorting of grains to the final packaging of the finished product. With advanced machinery and real-time monitoring systems, manufacturers can maintain continuous production with minimal downtime. This leads to higher output rates and the ability to meet growing market demands more effectively.
|
Consistent Quality and Reduced Human Error
| A fully automatic cereal processing line ensures consistent quality across all batches of production. Automated systems are designed to maintain precise control over each stage of the process, including cooking temperatures, shaping, and drying times. This level of precision minimizes variations and ensures that every batch of cereal meets the same high standards. Additionally, automation reduces the likelihood of human error, which can lead to product defects and waste. By minimizing human intervention, manufacturers can achieve a more uniform and reliable product.
|
Cost Savings and Return on Investment
| Investing in a fully automatic cereal processing line can lead to significant cost savings over time. While the initial investment may be substantial, the long-term benefits outweigh the costs. Automation reduces labor costs by minimizing the need for manual labor and allows for more efficient use of raw materials, reducing waste. Furthermore, the increased productivity and consistent quality achieved through automation can lead to higher sales and improved customer satisfaction. The return on investment for a fully automatic cereal processing line is typically realized within a few years of implementation.
|
Environmental and Sustainability Advantages | Fully automatic cereal processing lines also offer environmental and sustainability advantages. Automated systems are often more energy-efficient than traditional processing lines, reducing the overall energy consumption of the production facility. Additionally, precise control over the production process minimizes waste, leading to more efficient use of raw materials. This not only reduces the environmental impact of the manufacturing process but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products.
|
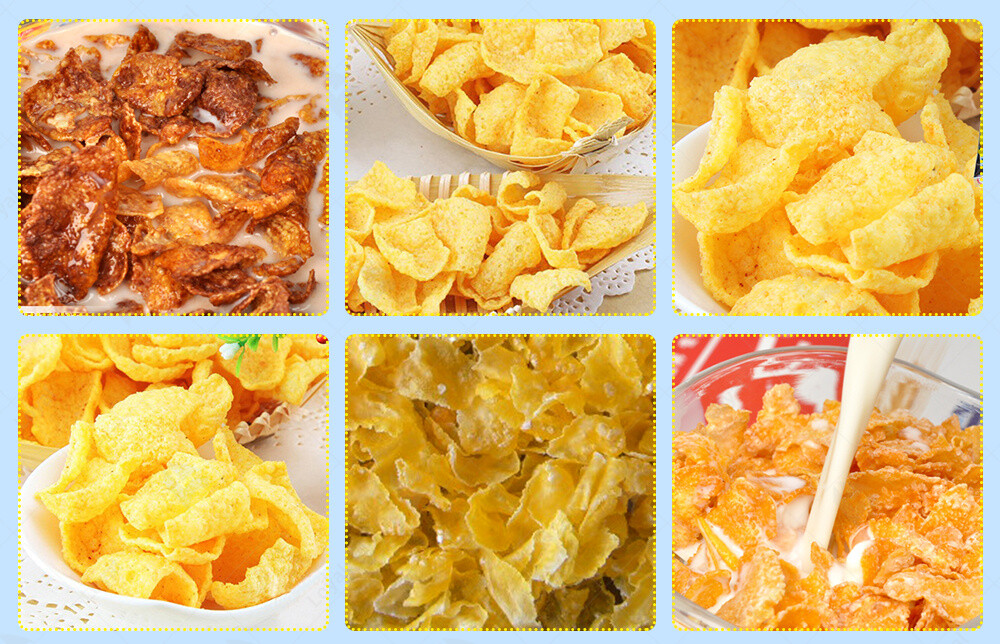

Key Technologies in Fully Automatic Cereal Processing Lines
Advanced Machinery and Equipment
The backbone of a fully automatic cereal processing line is its advanced machinery and equipment. These systems are designed to handle every stage of the production process with high precision and efficiency. Key pieces of equipment include:
- Grain Cleaners and Sorters:** These machines use sophisticated sorting technology to remove impurities and ensure only the highest quality grains are used in the cereal processing line. They play a crucial role in maintaining the purity and consistency of the raw materials.
- Extruders:** Used for cooking and shaping cereals, extruders apply controlled heat and pressure to transform raw grains into various cereal shapes and textures. They are essential for producing a wide range of cereal products, from cornflakes to puffed rice.
- Dryers and Coolers:** These machines ensure that the cereals are dried to the optimal moisture content, which is crucial for texture and shelf life. Proper drying is vital to prevent spoilage and maintain the crispness of the cereals.
- Packaging Machines:** Automating the final stage of production, these machines package cereals into boxes, bags, or pouches with consistent accuracy. They ensure that each package meets the same quality standards and is sealed for freshness.
Integration of IoT and Smart Sensors
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart sensors is a transformative technology in fully automatic cereal processing lines. IoT devices and sensors are embedded throughout the production line to collect real-time data on various parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and machine performance. This data is transmitted to a central control system where it is analyzed to optimize operations and ensure peak efficiency.
Smart sensors can detect and report anomalies, allowing for predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. For example, sensors can monitor the wear and tear on extruder components, alerting operators to perform maintenance before a breakdown occurs. This not only extends the lifespan of the machinery but also ensures continuous and reliable production.
Real-Time Monitoring and Data Analytics
Real-time monitoring and data analytics are critical components of a fully automatic cereal processing line. The data collected by IoT devices and smart sensors is analyzed in real-time to provide actionable insights. This allows manufacturers to make informed decisions quickly, enhancing the overall efficiency of the production process.
For instance, data analytics can identify patterns and trends that help optimize the cooking and drying stages, ensuring that the cereals are cooked and dried uniformly. It can also help in adjusting the settings of the packaging machines to reduce waste and improve packaging speed.
Examples of Cutting-Edge Technologies Used
Several cutting-edge technologies are commonly used in fully automatic cereal processing lines:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):** These technologies are employed to analyze vast amounts of data and improve decision-making processes. AI and ML algorithms can predict equipment failures, optimize production schedules, and enhance product quality.
- Robotic Automation:** Robots are increasingly being used for tasks such as sorting, packing, and palletizing cereals. They offer high precision and can operate continuously without fatigue.
- Blockchain Technology:** Some manufacturers are exploring the use of blockchain to enhance traceability and transparency in the supply chain. This technology can track the journey of cereals from raw materials to the final product, ensuring quality and safety.

Challenges and Considerations
Implementing and operating a fully automatic cereal processing line comes with several challenges and considerations that manufacturers need to address:
1.Initial Investment and Cost Barriers
One of the primary challenges of adopting a fully automatic cereal processing line is the substantial initial investment required. The cost of purchasing advanced machinery, integrating IoT systems, and training personnel can be significant. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate the return on investment (ROI) over the long term to justify the upfront costs.
2.Maintenance and Technical Support
Maintaining a fully automatic cereal processing line requires specialized technical knowledge and ongoing maintenance. Regular servicing of machinery, calibration of sensors, and software updates are essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime. Access to reliable technical support and spare parts is crucial for minimizing disruptions to production.
3.Training and Workforce Adaptation
Transitioning to a fully automatic cereal processing line necessitates training for operators and production staff. While automation reduces the need for manual labor, skilled personnel are still required to monitor operations, perform quality checks, and troubleshoot issues. Manufacturers must invest in training programs to equip their workforce with the necessary skills to operate and maintain automated systems effectively.
4.Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Food processing industries are subject to stringent regulatory standards and compliance requirements. Implementing automation in cereal processing must adhere to food safety regulations, hygiene standards, and environmental guidelines. Manufacturers must ensure that their automated systems meet all regulatory requirements and undergo regular inspections to maintain compliance.
5.Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Integrating a fully automatic cereal processing line with existing infrastructure and production processes can pose logistical challenges. Compatibility issues between new and old equipment, as well as software integration complexities, may arise. Manufacturers need to plan carefully and possibly retrofit existing facilities to accommodate automation seamlessly.
6.Scalability and Flexibility
While automation offers advantages in efficiency and productivity, ensuring scalability and flexibility is essential. Manufacturers must consider future growth opportunities and the ability of the automated system to adapt to changing market demands. Modular designs and flexible production lines can facilitate easier expansion and diversification of cereal product offerings.
7.Environmental Impact
Although automation can improve energy efficiency and reduce waste, manufacturers should also consider its overall environmental impact. Implementing sustainable practices, such as minimizing water usage and optimizing energy consumption, is crucial for reducing the carbon footprint of cereal processing operations.
Navigating these challenges requires careful planning, investment in technology and personnel, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Despite the complexities involved, the benefits of a fully automatic cereal processing line in terms of efficiency, quality, and competitiveness make it a worthwhile investment for forward-thinking manufacturers.

The Future of Cereal Processing Lines
The future of cereal processing lines is poised for continued innovation and advancement, driven by technological developments and evolving consumer preferences. Here are several key trends and developments shaping the future of this industry:
1.Emerging Technologies and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, cereal processing lines are likely to integrate more advanced technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play an increasingly crucial role in optimizing production processes. AI can analyze data patterns to improve efficiency, predict maintenance needs, and enhance product quality. Machine learning algorithms can adapt and optimize production parameters in real-time, maximizing yield and minimizing waste.
2.Enhanced Automation and Robotics
The trend towards greater automation and robotics in cereal processing lines is expected to continue. Robots equipped with advanced sensors and actuators can perform intricate tasks such as sorting, packing, and quality control with precision and efficiency. Collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human operators will become more prevalent, enhancing productivity and safety in the production environment.
3.Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability will remain a significant focus for the future of cereal processing lines. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices to reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and optimize resource usage. This includes implementing efficient water management systems, utilizing renewable energy sources, and exploring biodegradable packaging options. Sustainable practices not only align with consumer preferences for eco-friendly products but also contribute to long-term environmental stewardship.
4.Customization and Personalization
Consumer demand for customized and personalized cereal products is expected to grow. Cereal processing lines will need to be flexible enough to accommodate a variety of recipes, flavors, and nutritional profiles. Advanced production technologies, such as modular equipment and flexible manufacturing systems, will enable manufacturers to efficiently produce small batch sizes and quickly adapt to changing market trends. Personalized packaging and marketing strategies will also play a role in meeting consumer expectations for unique cereal experiences.
5.Data-driven Decision Making
The future of cereal processing lines will be increasingly data-driven. Manufacturers will leverage big data analytics to gain deeper insights into consumer preferences, market trends, and production efficiency. Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics will enable proactive decision-making, optimizing production schedules, and ensuring consistent product quality. Continuous improvement initiatives based on data analysis will drive operational excellence and competitiveness in the marketplace.
6.Globalization and Market Expansion
Globalization will continue to influence the cereal processing industry, with manufacturers expanding their operations to new markets and regions. Cereal processing lines will need to meet diverse regulatory requirements and cultural preferences while maintaining consistent product quality and safety standards. This may involve adapting equipment designs, optimizing supply chain logistics, and establishing local partnerships to support market entry and growth.

Reference
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites in the field of Industrial food machinery:
1. Food Engineering Magazine
Website: https://www.foodengineeringmag.com/
2.Food Processing Magazine
Website: https://www.foodprocessing.com/
3.Journal of Food Engineering
Website:https://www.journals.elsevier.com/journal-of-food-engineering
4. Food Manufacturing Magazine
Website:https://www.foodmanufacturing.com/
5. International Journal of Food Science & Technology
Website:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/