Everything You Need to Know About Bread Crumb Production
Introduction to Bread Crumb Production
Bread crumb production is a critical aspect of the food processing industry, providing essential ingredients for a variety of culinary applications. This process involves converting stale or fresh bread into crumbs through grinding and milling, ensuring a consistent texture and quality suitable for different recipes. Bread crumb production lines incorporate specialized machinery to efficiently produce large quantities of bread crumbs while maintaining stringent quality standards.
In modern bread crumb production, advanced technologies and equipment are utilized to optimize the process, from bread baking to crumb packaging. The goal is to create uniform, high-quality crumbs that meet the diverse needs of food manufacturers, restaurants, and home cooks. Understanding the intricacies of bread crumb production is essential for businesses aiming to deliver superior products in a competitive market.
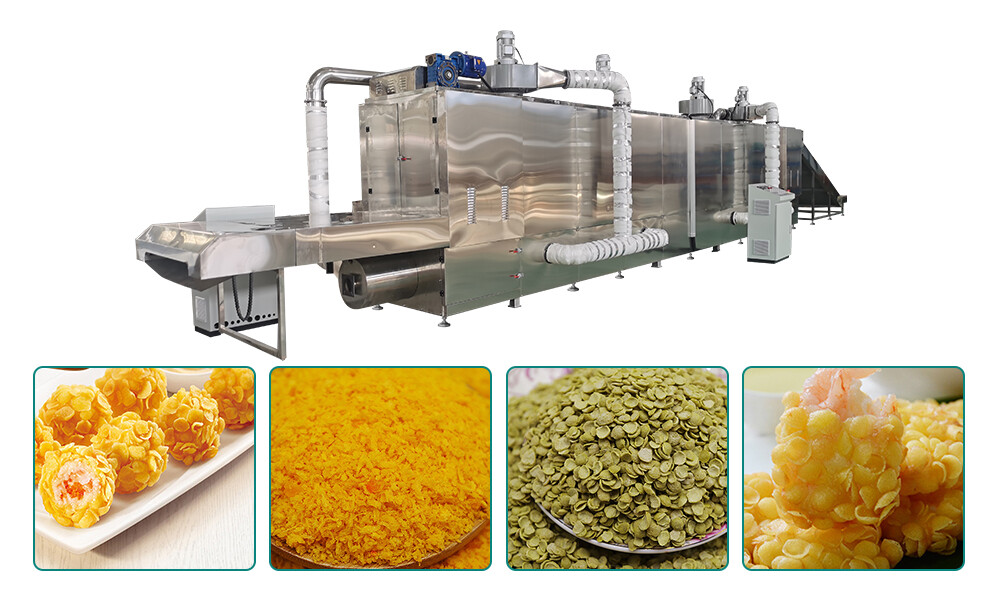

History and Evolution of Bread Crumbs
The history of bread crumbs dates back to ancient times when early civilizations discovered the utility of dried bread fragments. Initially, bread crumbs were made manually by grating stale bread, a practice that persisted for centuries. The evolution of bread crumbs is closely tied to the development of bread itself, as different cultures adopted unique methods to utilize leftover bread efficiently.
During the industrial revolution, bread crumb production began to transform with the introduction of mechanized equipment. Factories started using grinders and sifters to produce consistent and finer bread crumbs. This shift allowed for mass production and ensured a steady supply of bread crumbs for commercial use. As a result, bread crumbs became a staple ingredient in many cuisines, particularly for breading and binding purposes.
In the 20th century, the bread crumb industry saw significant advancements with the advent of automated production lines. These lines integrated various stages of production, from baking to grinding, into a cohesive system, greatly enhancing efficiency and product quality. Innovations such as vacuum cooling and advanced packaging solutions further revolutionized bread crumb production, making it possible to produce crumbs with longer shelf life and better texture.
Today, the industry continues to evolve with the introduction of cutting-edge technologies like computer-controlled baking ovens and high-speed milling machines. These advancements not only improve the consistency and quality of bread crumbs but also reduce production costs and environmental impact. The history of bread crumbs is a testament to the ingenuity and adaptability of the food processing industry.

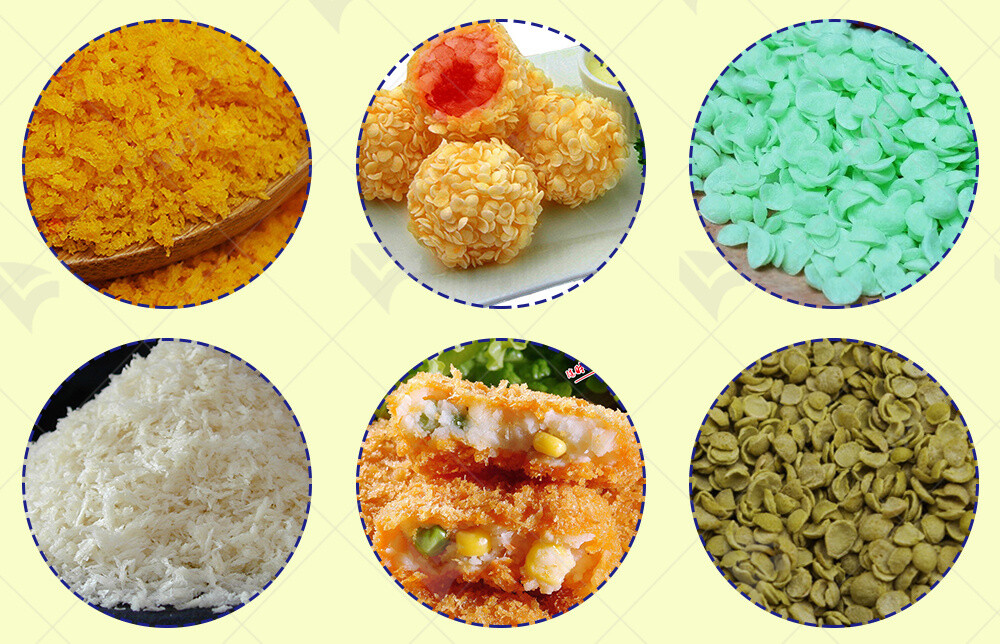
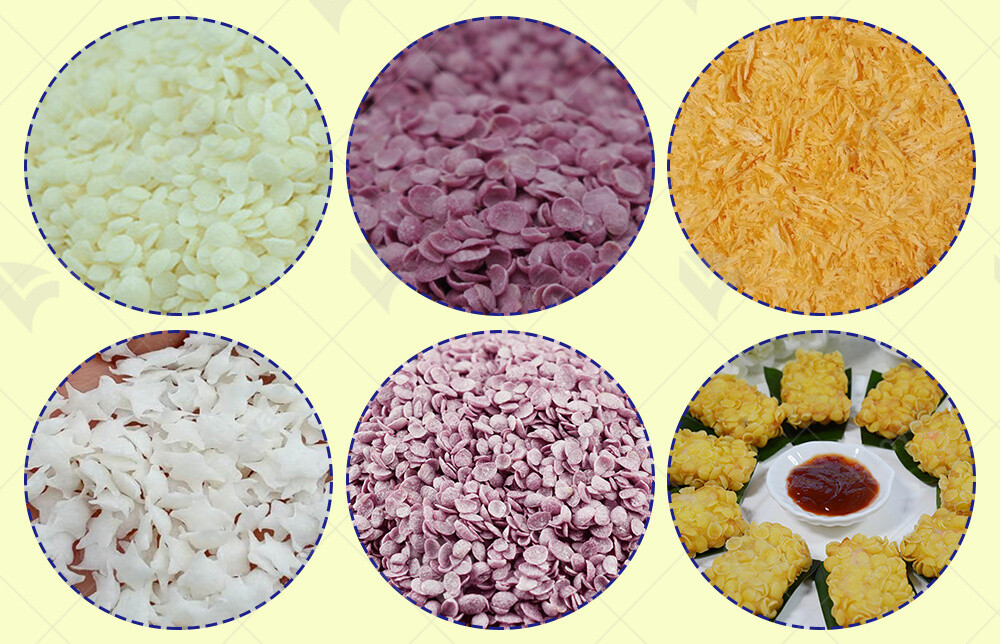
Types of Bread Crumbs and Their Applications
When it comes to bread crumbs, there are various types available, each with its unique characteristics and applications. As an expert in industrial food machinery, it's vital to understand these types to meet the diverse needs of customers in the food industry.
Type | Description | Applications |
| Plain Bread Crumbs | Fine or coarse crumbs made from plain bread | Coating for fried or baked foods, stuffing, toppings |
| Panko Bread Crumbs | Japanese-style crumbs with a light, airy texture | Ideal for crispy coatings, topping casseroles, seafood |
| Seasoned Crumbs | Bread crumbs seasoned with herbs and spices | Adds flavor to dishes such as chicken, fish, vegetables |
| Gluten-Free Crumbs | Made from gluten-free bread or alternative grains | Suitable for those with gluten intolerance or allergies |
Each type of bread crumbs offers unique advantages and applications, allowing for versatility in culinary creations. By understanding the different types available, industrial food machinery experts can cater to a wide range of consumer preferences and dietary needs.
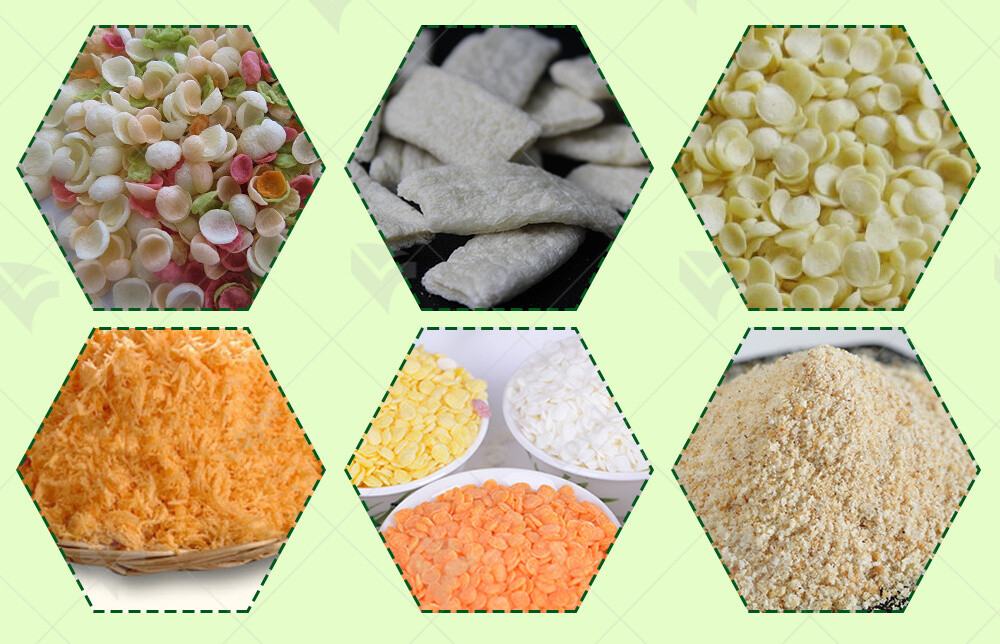

Importance of Bread Crumbs in Culinary Uses
Bread crumbs play a pivotal role in culinary applications, offering both functional and textural benefits to a wide range of dishes. In breading, bread crumbs provide a crisp and golden coating that enhances the visual and sensory appeal of fried foods. This makes them indispensable in the preparation of items like breaded chicken, fish, and vegetable cutlets. The quality and consistency of bread crumbs directly impact the final product, making bread crumb production a critical process in the food industry.
Beyond breading, bread crumbs are used as a binding agent in recipes such as meatballs, meatloaf, and stuffing. Their ability to absorb moisture and retain shape helps in achieving the desired texture and consistency. The versatility of bread crumbs extends to baking as well, where they are used to add a crunchy topping to casseroles, gratins, and desserts. This wide range of applications underscores the importance of reliable and high-quality bread crumb production.
In addition to their functional roles, bread crumbs contribute to the flavor profile of dishes. Seasoned bread crumbs, which include herbs, spices, and other flavorings, enhance the taste of various recipes. This aspect has led to the development of specialized production lines capable of producing seasoned and flavored bread crumbs, catering to the evolving tastes of consumers.
Overall, the significance of bread crumbs in culinary uses cannot be overstated. They not only improve the texture and appearance of dishes but also add to the overall dining experience. As a result, ensuring consistent and high-quality bread crumb production remains a priority for food manufacturers looking to meet consumer demands and maintain competitive advantage in the market.

Key Ingredients for Bread Crumb Production
As an expert in industrial food machinery, it's crucial to understand the key ingredients essential for bread crumb production. These ingredients play a significant role in determining the quality, texture, and flavor of the final product.
Ingredient | Description | Role in Production |
| Bread | Typically stale bread or bread scraps | Provides the base material for bread crumbs |
| Flour | All-purpose or bread flour | Helps bind the crumbs together and adds structure |
| Salt | Fine salt | Enhances flavor and acts as a preservative |
| Seasonings | Herbs, spices, garlic powder, onion powder, etc. | Adds flavor and versatility to the bread crumbs |
| Oil or Fat | Vegetable oil, butter, or margarine | Improves texture and aids in browning during baking |
| Yeast (optional) | Active dry yeast or instant yeast | Contributes to flavor development in certain types of crumbs |
Each ingredient in bread crumb production serves a specific purpose, whether it's providing texture, enhancing flavor, or extending shelf life. Understanding how these ingredients interact is essential for optimizing production processes and ensuring consistent quality.

Selecting the Right Bread for Crumbs
When it comes to bread crumb production, selecting the right type of bread is crucial for achieving the desired texture, flavor, and consistency in the final product. Various factors need to be considered to ensure optimal results. Below is a comprehensive guide to selecting the right bread for crumbs:
Bread Type | Characteristics | Best Application |
| White Bread | Soft texture, mild flavor | Ideal for general-purpose bread crumbs |
| Whole Wheat | Nutty flavor, dense texture | Suitable for health-conscious or rustic-style crumbs |
| Multigrain | Rich flavor, varied texture | Adds depth to breadcrumbs, great for savory dishes |
| Baguette | Crisp crust, airy interior | Perfect for creating crispy coatings or toppings |
| Sourdough | Tangy flavor, chewy texture | Adds complexity to breadcrumbs, great for gourmet dishes |
When selecting bread for crumbs, bread crumb production experts recommend considering the intended use of the crumbs. For example, softer bread varieties like white or whole wheat are excellent choices for general-purpose breadcrumbs used in coatings or fillings. On the other hand, crustier bread such as baguette or sourdough works well for creating crunchy toppings or adding texture to dishes.
Furthermore, the freshness of the bread is paramount. Stale bread is preferred for bread crumb production as it absorbs coatings and seasonings more effectively, resulting in crispier and more flavorful crumbs. However, if stale bread is not available, fresh bread can be dried out in a low-temperature oven to achieve a similar texture.
It's also essential to consider any dietary restrictions or preferences when selecting bread for crumbs. Gluten-free or artisanal bread varieties may be preferred by some consumers, requiring manufacturers to offer a diverse range of options to cater to different dietary needs.

Mixing and Dough Preparation Equipment
In bread crumb production, mixing and dough preparation equipment play a pivotal role in achieving the desired texture and consistency of the final product. Industrial mixers are commonly used to combine ingredients such as flour, water, yeast, and other additives. These mixers ensure thorough blending while maintaining precise control over dough consistency.
Once the dough is mixed, it undergoes a series of conditioning processes to develop its gluten structure. This stage is crucial for achieving the desired texture and strength in the bread crumb. Dough dividers and rounders are used to portion the dough into uniform sizes, ensuring consistent baking results.
After portioning, the dough is typically left to rest and ferment, allowing flavors to develop and the gluten to relax. This stage is essential for achieving optimal texture and flavor in the final product.
Bread Baking Ovens for Crumb Production
Bread baking ovens are integral to the bread crumb production process, as they are responsible for transforming the prepared dough into fully baked loaves. Bread baking ovens come in various types, including deck ovens, rack ovens, and tunnel ovens, each offering unique advantages depending on the production scale and desired characteristics of the bread crumb.
Deck ovens are commonly used for artisanal bread production, allowing for precise control over temperature and humidity levels. Rack ovens are ideal for high-volume production, with multiple racks accommodating large batches of dough simultaneously. Tunnel ovens are designed for continuous baking processes, offering efficient throughput and consistent results.
Regardless of the oven type, precise control over baking parameters such as temperature, steam injection, and airflow is essential for achieving uniform baking and desired crust characteristics in the bread crumb.

Cooling and Drying Systems in Bread Crumb Production
After baking, the bread loaves undergo a cooling and drying process to remove excess moisture and ensure proper shelf stability. Cooling racks or conveyors are used to transfer the freshly baked loaves from the oven to the cooling area, where they are allowed to cool to room temperature gradually.
Once cooled, the bread loaves are typically sliced or shredded into smaller pieces before undergoing the drying process. Drying can be achieved through various methods, including air drying, convection drying, or mechanical drying using specialized equipment such as belt dryers or fluidized bed dryers.
Proper drying is crucial for reducing the moisture content of the bread crumbs to the desired level, preventing microbial growth and ensuring long-term storage stability. Additionally, drying enhances the crispiness and texture of the bread crumbs, making them ideal for use in various culinary applications.
In conclusion, the mixing and dough preparation equipment, bread baking ovens, and cooling and drying systems are essential components of the bread crumb production process. Understanding the functionality and importance of these equipment and processes is key to achieving high-quality bread crumbs with consistent texture and flavor.

Maintenance and Cleaning of Production Equipment
Proper maintenance and cleaning of production equipment are vital for the smooth operation of bread crumb production lines. Regular maintenance ensures that machinery operates efficiently and reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns. It involves routine inspections, lubrication, and replacement of worn-out parts to keep the equipment in optimal condition.
Effective cleaning protocols are equally important to prevent contamination and maintain food safety standards. Bread crumb production involves handling perishable ingredients, making it crucial to clean equipment thoroughly to remove any residual dough, crumbs, or bacteria. Automated cleaning systems, such as Clean-In-Place (CIP) technology, can significantly enhance the efficiency and thoroughness of the cleaning process.
Maintenance schedules should be meticulously planned to minimize production downtime. This involves conducting preventive maintenance during off-peak hours or scheduled shutdowns to avoid disrupting the production flow. Additionally, training staff on proper maintenance and cleaning procedures is essential to ensure consistency and adherence to safety protocols.

Innovations in Bread Crumb Production Technology
The field of bread crumb production technology has seen significant innovations aimed at improving efficiency, quality, and sustainability. One of the key advancements is the development of energy-efficient baking ovens that use less energy while maintaining optimal baking conditions. These ovens incorporate advanced insulation materials and heat recovery systems to reduce energy consumption and operating costs.
Another innovation is the use of high-precision milling and grinding equipment. Modern mills can produce bread crumbs with consistent particle sizes, which is crucial for specific culinary applications. These mills often feature adjustable settings, allowing manufacturers to produce a variety of crumb textures from coarse to fine, catering to diverse market needs.
Sustainability is also a driving force behind technological advancements in bread crumb production. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as using recyclable packaging materials and reducing waste through improved process efficiencies. Some production lines now include systems for reclaiming and reusing by-products, contributing to a more sustainable production cycle.
These innovations are setting new standards in the bread crumb production industry, enabling manufacturers to meet growing demand while adhering to stringent quality and sustainability criteria. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements that will shape the future of bread crumb manufacturing.
Reference
1.Baker Perkins - bakerperkins.com
2.GEA Group - gea.com
3.Heat and Control - heatandcontrol.com
4.Hosokawa Micron - hosokawamicron.com
5.Fritsch Group - fritsch-group.com