Unlock The Secret To Nutrition Powder and Baby Rice Powder Process Line
Introduction
Welcome to our expert guide on Nutrition Powder and Baby Rice Powder Process Lines. In the realm of industrial food machinery, understanding the intricacies of producing nutrition powder and baby rice powder is paramount. These products play a crucial role in meeting the dietary needs of infants and ensuring high nutritional standards.
The process of developing nutrition powder and baby rice powder involves sophisticated machinery and precise techniques. From selecting the right raw materials to optimizing blending and extrusion processes, each step contributes to the quality and safety of the final product. As industrial food machinery specialists, we explore the essential components required for these production lines, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards and embracing technological innovations that enhance efficiency and consistency.
Throughout this guide, we'll uncover the secrets behind establishing and refining Nutrition Powder and Baby Rice Powder Process Lines. Whether you're new to the industry or seeking to enhance your existing operations, this resource aims to provide authoritative insights and practical knowledge to propel your success in this specialized field.
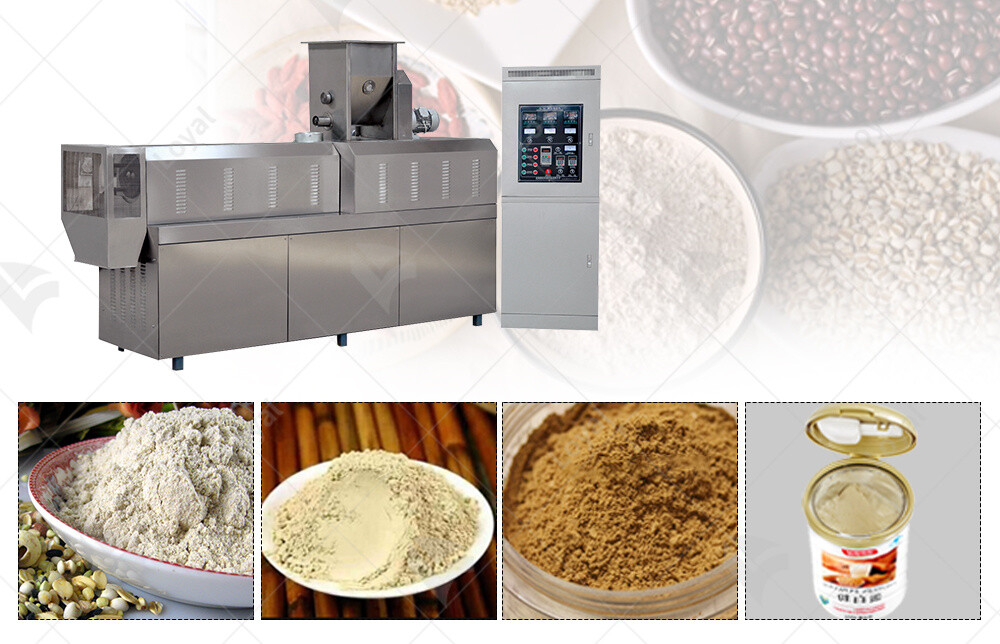

Key Components of Nutrition Powder Production Line
In the realm of industrial food machinery, designing an efficient Nutrition Powder Production Line requires meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of the process. Let's delve into the essential components that form the backbone of these sophisticated production lines.
1. Raw Material Handling Systems
The process begins with the selection and handling of raw materials, which are crucial for the nutritional content and quality of the final product. Raw material handling systems include conveyors, elevators, and storage silos designed to maintain ingredient integrity and prevent contamination.
2. Mixing and Blending Units
Once the raw materials are prepared, they undergo mixing and blending processes to achieve uniformity and consistency in the nutrition powder formulation. High-capacity mixers and blenders equipped with precision controls ensure optimal blending of ingredients, including vitamins, minerals, and additives.
3. Extrusion Systems
Extrusion plays a pivotal role in transforming the blended ingredients into a desired form, typically through a high-pressure extruder. This process not only shapes the nutrition powder but also enhances its digestibility and shelf stability.
4. Drying and Cooling Equipment
After extrusion, the product undergoes drying to remove moisture and achieve the desired texture and shelf life. Advanced drying systems, such as spray dryers or fluidized bed dryers, efficiently remove water while preserving nutritional integrity. Cooling units then ensure the product reaches ambient temperature before packaging.
5. Packaging Machinery
Packaging is the final step in the Nutrition Powder Production Line, where automated packaging machines fill and seal the product into various formats, including sachets, pouches, or bulk containers. These machines are equipped with weight sensors and quality control systems to ensure accurate filling and packaging compliance.
6. Quality Control and Monitoring Systems
Throughout the production process, robust quality control measures are essential to uphold product safety and consistency. Advanced monitoring systems, including spectroscopy and chromatography tools, verify nutritional content and detect any deviations from specifications.
7. Automation and Control Systems
Modern Nutrition Powder Production Lines leverage automation and control systems to optimize efficiency and reduce human error. PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems coordinate and regulate equipment operations, ensuring seamless integration and precise process control.

Benefits of Using a Nutrition Powder and Baby Rice Powder Process Line
Benefits of Using a Nutrition Powder and Baby Rice Powder Process Line |
| 1. Enhanced Efficiency |
| Utilizes automated systems for precise blending and extrusion. |
| Reduces production time and labor costs. |
| 2. Consistent Product Quality |
| Ensures uniform texture and nutritional content. |
| Minimizes variability in product output. |
| 3. Regulatory Compliance |
| Meets FDA and international standards for food safety. |
| Adheres to stringent quality control measures. |
| 4. Cost-Effectiveness |
| Optimizes raw material usage and reduces waste. |
| Lower operational costs over time due to efficiency gains. |
| 5. Flexibility in Production |
| Capable of producing various formulations and packaging options. |
| Adjusts easily to meet changing market demands. |
| 6. Improved Safety and Hygiene |
| Minimizes contamination risks through automated handling. |
| Enhances workplace safety with integrated safety features. |
| 7. Technological Advancements |
| Integrates latest technological innovations for higher productivity. |
| Allows for remote monitoring and control of production processes. |
| 8. Scalability and Growth |
| Easily scales production capacity to meet growing demand. |
| Supports expansion into new markets with consistent quality assurance. |

Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process
In the realm of industrial food machinery, mastering the step-by-step manufacturing process for Nutrition Powder and Baby Rice Powder is crucial for ensuring product quality and efficiency.
1. Raw Material Preparation
Key Steps: Begin by carefully selecting and handling raw materials such as rice, grains, vitamins, and minerals. This initial step sets the foundation for the nutritional content and quality of the final product. LSI Keywords: food ingredients, raw material handling.
2. Mixing and Blending
Key Steps: Once the raw materials are prepared, they undergo precise mixing and blending. This process ensures uniform distribution of nutrients and enhances the consistency of the powder. Modern blending equipment with automated controls ensures accuracy and efficiency. LSI Keywords: blending techniques, formulation.
3. Extrusion and Shaping
Key Steps: After blending, the mixture is extruded through specialized equipment. Extrusion involves applying high pressure and heat to create a uniform texture and shape. This step is critical for optimizing the digestibility and nutritional value of the powder. LSI Keywords: extrusion process, shaping techniques.
4. Drying
Key Steps: The extruded product then undergoes drying to reduce moisture content. Various drying methods, including spray drying and fluidized bed drying, are employed to achieve the desired consistency and shelf stability. LSI Keywords: drying methods, moisture control.
5. Cooling
Key Steps: Once dried, the product is cooled to ambient temperature. Cooling ensures product integrity and prepares it for subsequent processing or packaging stages. Advanced cooling systems help maintain product quality and reduce production time. LSI Keywords: cooling systems, product handling.
6. Packaging
Key Steps: The final step involves packaging the nutrition powder into consumer-ready formats. Packaging machinery with automated filling and sealing capabilities ensures hygienic and efficient packaging. Different packaging materials and formats are chosen based on market preferences and regulatory requirements. LSI Keywords: packaging machinery, packaging materials.
7. Quality Control
Key Steps: Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented to uphold product safety and consistency. Advanced testing methods and quality assurance protocols verify nutritional content, microbiological safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. LSI Keywords: quality assurance, regulatory compliance.
8. Automation and Monitoring
Key Steps: Automation plays a pivotal role in optimizing the manufacturing process. Automated systems and monitoring technologies oversee production parameters, detect deviations, and ensure continuous operation. This integration of technology enhances efficiency, reduces human error, and improves overall product quality. LSI Keywords: automation technology, process monitoring.
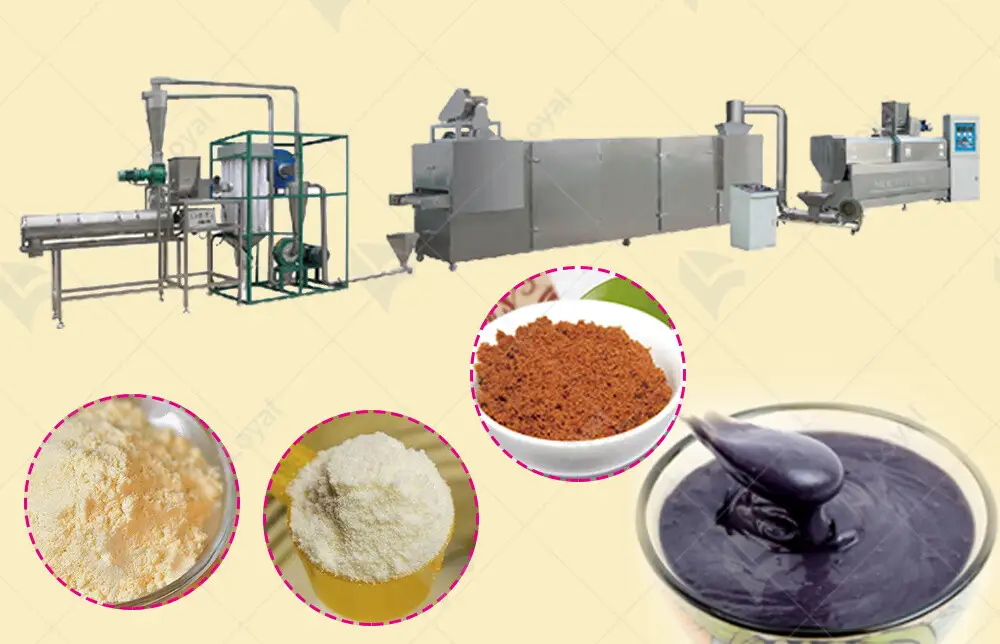

Quality Control Measures
Quality control is paramount in the production of nutrition powder and baby rice powder process lines. To ensure consistency and safety, stringent measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process. Here’s a comprehensive look at the key aspects of quality control:
1. Raw Material Selection and Testing:
Effective quality control begins with the careful selection of raw materials. Ingredients must meet specific criteria for purity, nutritional content, and absence of contaminants. Rigorous testing protocols, including microbiological analysis and chemical composition tests, are conducted to verify compliance with industry standards.
2. Process Monitoring and Optimization:
Continuous monitoring of production processes is essential to maintain product quality. Advanced sensors and monitoring systems track parameters such as temperature, moisture levels, and mixing times. Any deviations from optimal conditions trigger immediate corrective actions to prevent quality issues.
3. Hygienic Design and Maintenance:
Hygiene is non-negotiable in food processing. Process lines are designed with stainless steel surfaces and smooth, easily cleanable components to minimize bacterial growth and cross-contamination risks. Regular maintenance schedules ensure equipment remains in peak condition, reducing downtime and ensuring consistent production output.
4. Testing and Validation of Finished Products:
Finished products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet safety and quality standards before reaching consumers. Tests include sensory evaluation, nutritional analysis, and shelf-life studies to verify stability and compliance with label claims. Results are documented to facilitate traceability and regulatory compliance.
5. Training and Quality Assurance Protocols:
Quality control is a collaborative effort involving skilled personnel trained in Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Continuous training programs equip staff with the knowledge and skills to uphold stringent quality assurance protocols. Regular audits and internal inspections further validate adherence to quality standards.

Technological Innovations in Production
The production of Nutrition Powder and Baby Rice Powder has evolved significantly with the integration of advanced technological innovations in industrial food machinery. These innovations play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency, ensuring product quality, and meeting consumer demands. Let's explore the key technological innovations used in this specialized manufacturing process:
1. Automated Mixing and Blending Systems
Key Innovations: Automated mixing and blending systems utilize precision controls and algorithms to achieve consistent formulation of nutrition powders. These systems optimize ingredient dispersion and ensure uniformity in nutritional content. LSI Keywords: automated blending, precision control.
2. High-Pressure Extrusion Technology
Key Innovations: High-pressure extrusion technology enables the precise shaping of nutrition powders into desired forms. This technology enhances product texture, digestibility, and shelf stability by applying controlled pressure and temperature during extrusion. LSI Keywords: extrusion technology, shaping precision.
3. Advanced Drying Techniques
Key Innovations: Advanced drying techniques such as spray drying and freeze drying preserve the nutritional integrity of ingredients while efficiently removing moisture. These methods enhance product shelf life and maintain sensory attributes without compromising nutritional value.
4. IoT-enabled Monitoring and Control Systems
Key Innovations: IoT-enabled monitoring and control systems provide real-time data insights into production parameters. Manufacturers can remotely monitor equipment performance, adjust settings, and preemptively identify potential issues to optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime. 5. Robotics and Automation Integration
Key Innovations: Robotics and automation technologies streamline production processes by automating repetitive tasks such as packaging and palletizing. These technologies improve operational efficiency, reduce human error, and ensure consistent product quality throughout the production line. LSI Keywords: robotics in food production, automated packaging.
6. Quality Control with AI and Machine Learning
Key Innovations: AI and machine learning algorithms enhance quality control measures by analyzing data from sensors and cameras in real-time. These technologies detect anomalies, predict potential quality issues, and optimize process parameters to maintain high product standards and regulatory compliance. LSI Keywords: AI in quality control, machine learning in manufacturing.

Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
In the realm of nutrition powder and baby rice powder process lines, the future outlook is shaped by advancing technology and evolving consumer preferences. Industrial food machinery continues to innovate, meeting the demand for efficient and hygienic production processes.
Key Trends:
1. Automation Advancements: Automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing production efficiency and maintaining product quality. Advanced robotics and AI-driven systems are increasingly integrated into process lines, ensuring precision and consistency.
2. Focus on Hygiene and Safety: With growing concerns over food safety, process lines are incorporating state-of-the-art sanitation protocols. Stainless steel materials and automated cleaning systems minimize contamination risks, meeting stringent regulatory standards.
3. Customization and Flexibility: Consumer preferences for personalized nutrition products drive the need for versatile production capabilities. Modular designs allow manufacturers to adjust production lines swiftly, accommodating varied formulations and packaging options.
4. Sustainability Initiatives: Environmental sustainability is a critical focus area. Process lines are adopting energy-efficient technologies and reducing waste through improved recycling and reuse practices.
5. Digital Integration: Industry 4.0 principles are revolutionizing production management. IoT-enabled sensors gather real-time data, optimizing operational efficiency and predictive maintenance schedules.

References
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites on industrial Nutrirional Powder production:
1.Science.gov
Website: [https://www.science.gov]
2.Data.gov
Website: [https://www.data.gov]
3.SpringerLink
Website: [https://link.springer.com/]
4.WorldWideScience.org
Website: [https://www.worldwidescience.org]
5.DOAJ (Directory of Open Access Journals)
Website: [https://www.doaj.org]