The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Microwave Ovens in 2024
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of food processing technology, industrial microwave ovens have emerged as indispensable tools for efficient and precise heating, drying, and cooking of a wide range of food products. As we delve into the ultimate guide to industrial microwave ovens in 2024, it becomes evident that these innovative appliances play a pivotal role in enhancing productivity, ensuring food safety, and maintaining product quality in various industrial settings.
Industrial microwave ovens harness the power of electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range to heat and cook food rapidly and uniformly. Unlike conventional ovens that rely on convection or conduction heating, microwave ovens penetrate the food directly, resulting in significantly reduced cooking times and improved energy efficiency.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will explore the working principles, applications, technological advancements, and considerations associated with industrial microwave ovens. By delving into these aspects, we aim to provide valuable insights into the capabilities and potential of industrial microwave ovens in meeting the diverse needs of the food processing industry in 2024 and beyond.

How Industrial Microwave Ovens Work
Industrial microwave ovens are complex devices that use microwave radiation to heat and cook food efficiently and quickly. Unlike conventional ovens that rely on convection or conduction heating, industrial microwave ovens work on the principle of dielectric heating.
At the heart of an industrial microwave oven is the magnetron, a vacuum tube that generates microwave radiation at a frequency of approximately 2.45 GHz. The microwave radiation is then directed into the oven cavity where it interacts with the food. When food is exposed to microwave radiation, water molecules within the food absorb energy and oscillate rapidly. The stirring of water molecules generates heat throughout the food, resulting in even and rapid heating.
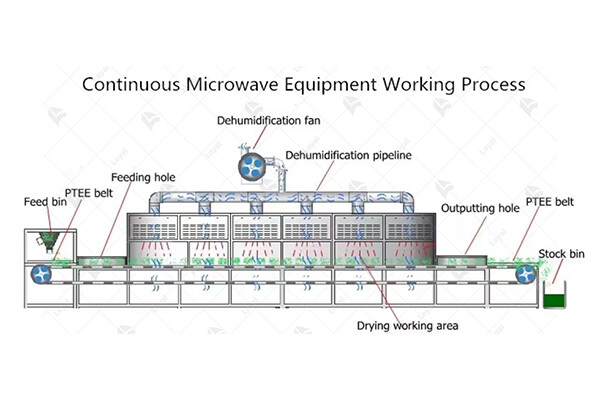
Key Components of Industrial Microwave Ovens
Industrial microwave ovens are sophisticated machines designed for efficient and precise heating, drying, and cooking of various materials. Understanding the key components of these ovens is essential for comprehending their functionality and optimizing their performance. Below are the primary components found in industrial microwave ovens:
1. Magnetron:
The magnetron is the heart of an industrial microwave oven. It generates high-frequency microwaves by converting electrical energy into electromagnetic radiation. These microwaves are then directed into the cooking chamber, where they interact with the food or material being processed, causing the molecules to vibrate and generate heat.
2. Waveguide:
The waveguide is a hollow metal tube or channel that guides the microwaves from the magnetron to the cooking chamber. It ensures that the microwaves are directed efficiently and uniformly into the oven cavity, minimizing energy loss and maximizing heating efficiency. Waveguides are often made of materials such as stainless steel or copper to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated during operation.
3. Stirrer Fan:
Many industrial microwave ovens are equipped with a stirrer fan, also known as a mode stirrer. This component is responsible for distributing the microwaves evenly throughout the cooking chamber, ensuring uniform heating of the material. By continuously rotating or oscillating, the stirrer fan helps to prevent hot spots and cold spots within the oven cavity, resulting in consistent and thorough heating.
4. Control Panel and User Interface:
The control panel and user interface allow operators to program and monitor the operation of the industrial microwave oven. It typically includes digital displays, buttons, and knobs for setting parameters such as power level, time, and temperature. Advanced models may feature touchscreen interfaces or computerized control systems for precise control and automation of the cooking process.
5. Safety Interlocks:
Industrial microwave ovens are equipped with safety interlocks to prevent accidents and ensure operator safety. These interlocks may include door switches that disable the microwave when the door is open, overheat sensors that shut down the oven in case of excessive temperature rise, and radiation leakage detectors to monitor and maintain safe levels of microwave emissions.
6. Cooling System:
Due to the high temperatures generated during operation, industrial microwave ovens require effective cooling systems to prevent overheating and ensure reliable performance. Cooling systems typically include fans, heat sinks, and air vents to dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating conditions within the oven.

Comparison and advantages of microwave technology and traditional drying methods
Aspect | Industrial Microwave Ovens | Traditional Drying Methods |
Drying Time | Significantly shorter drying times | Longer drying times, often requiring hours or days |
Energy Efficiency | Higher energy efficiency, reducing operational costs | Lower energy efficiency, leading to higher operational costs |
Temperature Control | Precise temperature control, minimizing the risk of over-drying or overheating | Limited temperature control, increasing the risk of product damage or uneven drying |
Quality Preservation | Retains product quality, flavor, and nutrients | May lead to degradation of product quality and loss of nutrients |
Space Requirement | Compact design, suitable for smaller facilities or limited spaces | Requires larger drying chambers or facilities |
Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon footprint and environmental impact | Higher environmental impact due to energy consumption and emissions |
Flexibility and Versatility | Offers flexibility to dry a wide range of products with varying characteristics | Limited versatility, often tailored to specific product types or materials |
Maintenance and Safety | Generally requires less maintenance and offers improved safety features | May require frequent maintenance and pose safety risks associated with high temperatures or combustion |
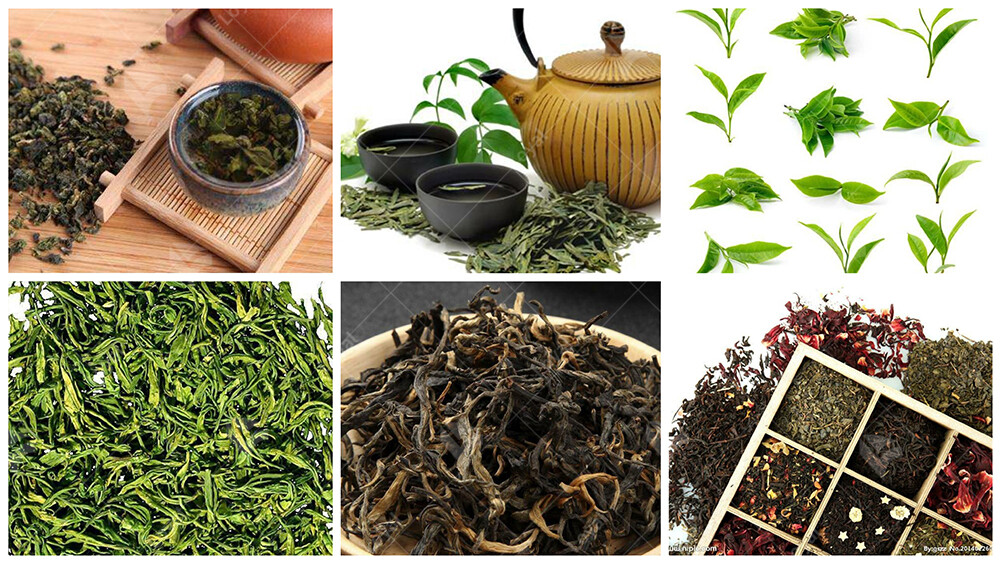

Types of Industrial Microwave Ovens
When it comes to industrial microwave ovens, various types are available on the market, each catering to specific needs and requirements. Below is a concise overview of the common types of industrial microwave ovens used in 2024:
Type of Industrial Microwave Oven | Description |
Batch Microwave Oven | - Designed for small to medium-scale production<br>- Ideal for processing batch quantities of food products<br>- Offers flexibility and ease of operation |
Continuous Microwave Oven | - Suited for large-scale production and continuous processing<br>- Features conveyor belts or other continuous feed mechanisms<br>- Offers high throughput and efficiency |
Tunnel Microwave Oven | - Specifically designed for uniform and consistent heating of products on a conveyor belt<br>- Ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control<br>- Offers scalability and automation capabilities |
Hybrid Microwave Oven | - Combines microwave and conventional heating methods<br>- Offers versatility for a wide range of food processing applications<br>- Allows for precise control over heating and cooking processes |
Each type of industrial microwave oven has its advantages and is suitable for different production environments and applications. Understanding the unique features and capabilities of each type is essential for selecting the most suitable option for your specific needs in 2024.
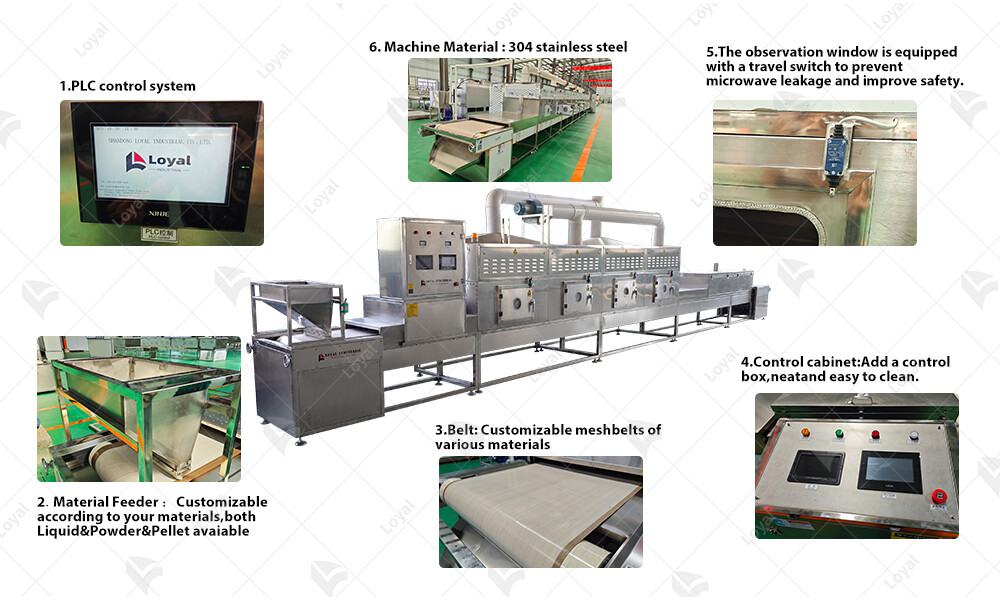

Technical parameters
| Technical Parameters Of Continuous Microwave Dryer Industrial Microwave Drying Machine | |||||
| Model | Size LWH(Can be customized according to the customer's requirements) | Output power | Dewaterability | Sterilization capacity | Baking and Roasting capacity (Depends on different raw material) |
| LY-10KW | 5000mm825mm1750mm | ≥10KW | 10KG/Hour | 100KG/Hour | 30-50KG/Hour |
| LY-20KW | 8000mm825mm1750mm | ≥20KW | 20KG/Hour | 200KG/Hour | 60-100KG/Hour |
| LY-30KW | 8500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥30KW | 30KG/Hour | 300KG/Hour | 90-150 KG/Hour |
| LY-40KW | 10000mm1160mm1750mm | ≥40KW | 40KG/Hour | 40KG/Hour | 120-200KG/Hour |
| LY-50KW | 12500mm1160mm1750mm | ≥50KW | 50KG/Hour | 500KG/Hour | 150-250KG/Hour |
| LY-60KW | 13500mm1450mm1750mm | ≥60KW | 60KG/Hour | 600KG/Hour | 180-300KG/Hour |
| LY-70KW | 13500mm1500mm1750mm | ≥70KW | 70KG/Hour | 700KG/Hour | 210-350KG/Hour |
| LY-80KW | 13500mm1650mm1750mm | ≥80KW | 80KG/Hour | 800KG/Hour | 240-400KG/Hour |
| LY-100KW | 16800mm1650mm1750mm | ≥100KW | 100KG/Hour | 1000KG/Hour | 300-500KG/Hour |
| LY-150KW | 22400mm1850mm1750mm | ≥150KW | 150KG/Hour | 1500KG/Hour | 450-750KG/Hour |
| LY-200KW | 27000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥250KW | 250KG/Hour | 2500KG/Hour | 750-1250/Hour |
| LY-300KW | 32000mm1850mm1750mm | ≥300KW | 300KG/Hour | 3000KG/Hour | 900-1500KG/Hour |
| Power Supply | 380V±10% 50Hz±1% Three-Phase Five-Wire | ||||
| Microwave Output Frequency | 2450±50Mhz | ||||
| Microwave Input Apparent Power | ≤168Kva | ||||
| Microwave Output Power | ≥120Kw | ||||
| Microwave Power Adjustment Range | 0-30Kw(Adjustable) | ||||
| Ambient Temperature | -5-40°C | ||||
| Relative Humidity | ≤80%, Surrounding Environment:No Corrosive Gas, Conductive Dust And Explosive Gas | ||||
| Transmission Speed | 0-10m/Min(Adjustable) | ||||
Technological Progress and Innovation of Industrial Microwave Ovens
In 2024, industrial microwave ovens continue to undergo significant technological progress and innovation, transforming the landscape of food processing and other industries. These advancements are driven by the constant pursuit of efficiency, quality, and sustainability.
1. Integration of Automation and AI:
Industrial microwave ovens are increasingly integrating automation and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. This enables precise control over heating processes, ensuring uniformity and consistency in product quality. AI algorithms analyze data in real-time, allowing for adaptive adjustments to optimize energy usage and reduce processing time.
2. Enhanced Heating Mechanisms:
New heating mechanisms have been developed to overcome the limitations of traditional microwave heating. Technologies such as multi-mode heating and frequency modulation allow for more precise control over heating profiles, resulting in improved uniformity and efficiency. These advancements enable industrial microwave ovens to handle a wider range of products with varying sizes and properties.
3. Improved Safety Features:
Safety remains a paramount concern in industrial settings. Manufacturers have enhanced the safety features of industrial microwave ovens to meet rigorous standards and regulations. Innovations such as automatic shut-off systems, temperature monitoring, and leak detection ensure safe operation and minimize risks of accidents or equipment damage.
4. IoT Connectivity and Remote Monitoring:
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized industrial equipment, including microwave ovens. Industrial microwave ovens equipped with IoT sensors and connectivity capabilities allow for remote monitoring and control. Operators can access real-time data, receive alerts for maintenance or troubleshooting, and optimize oven performance from anywhere, enhancing operational efficiency and uptime.
5. Customization and Flexibility:
Industrial microwave oven manufacturers recognize the diverse needs of their customers and offer greater customization and flexibility in oven design and configuration. Modular designs, adjustable power levels, and versatile heating profiles enable tailored solutions for specific applications and production requirements. This flexibility allows industries to optimize their processes and achieve higher productivity.
6. Sustainable Practices:
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, industrial microwave oven manufacturers are implementing eco-friendly practices in their designs and operations. Energy-efficient components, recyclable materials, and reduced carbon footprints are key focus areas. Additionally, innovations such as heat recovery systems and closed-loop cooling systems further minimize environmental impact and contribute to a greener future.

Precautions for Selecting and Implementing Industrial Microwave Ovens
When it comes to selecting and implementing industrial microwave ovens in your food processing operations, careful consideration and adherence to best practices are paramount. Here are some essential precautions to keep in mind:
1. Capacity and Power Requirements:
Before purchasing an industrial microwave oven, thoroughly assess your production needs and the volume of food products to be processed. Ensure that the oven's capacity aligns with your requirements and that its power rating is sufficient to handle your workload efficiently.
2. Compatibility with Food Products:
Consider the specific characteristics of the food products you intend to process in the microwave oven. Certain foods may require specialized equipment or modifications to ensure optimal results and prevent overheating or undercooking.
3. Safety Features and Regulations:
Prioritize industrial microwave ovens equipped with robust safety features, such as automatic shut-off mechanisms, temperature sensors, and interlocking doors. Additionally, ensure compliance with relevant industry regulations and standards to guarantee the safety of your personnel and products.
4. Installation and Calibration:
Proper installation and calibration are essential for the optimal performance of industrial microwave ovens. Follow manufacturer guidelines meticulously and consider enlisting the assistance of qualified technicians to ensure accurate setup and calibration.
5. Maintenance and Cleaning Protocols:
Establish regular maintenance schedules and cleaning protocols to keep your industrial microwave oven in peak condition. Routine inspections, component replacements, and thorough cleaning of interior surfaces are essential to prevent contamination and ensure consistent performance.
6. Training and Operator Competency:
Provide comprehensive training to personnel responsible for operating industrial microwave ovens. Ensure that operators understand proper usage, safety protocols, and emergency procedures to minimize risks and maximize efficiency.
7. Monitoring and Quality Control:
Implement robust monitoring and quality control measures to maintain product consistency and safety. Regularly monitor microwave oven performance, conduct product testing, and address any deviations promptly to prevent quality issues or product recalls.
8. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability:
Opt for energy-efficient industrial microwave ovens equipped with features such as variable power settings and automatic power adjustment. Additionally, explore opportunities to integrate sustainable practices into your microwave oven operations, such as utilizing renewable energy sources and minimizing waste.
9. Integration with Existing Processes:
Ensure seamless integration of industrial microwave ovens with existing production processes and equipment. Evaluate compatibility with other machinery, workflow efficiency, and potential bottlenecks to optimize overall operational performance.
10. Supplier Reputation and Support:
Choose reputable suppliers with a proven track record of delivering high-quality industrial microwave ovens and reliable customer support. Consider factors such as warranty coverage, technical assistance, and responsiveness to ensure a positive long-term partnership.
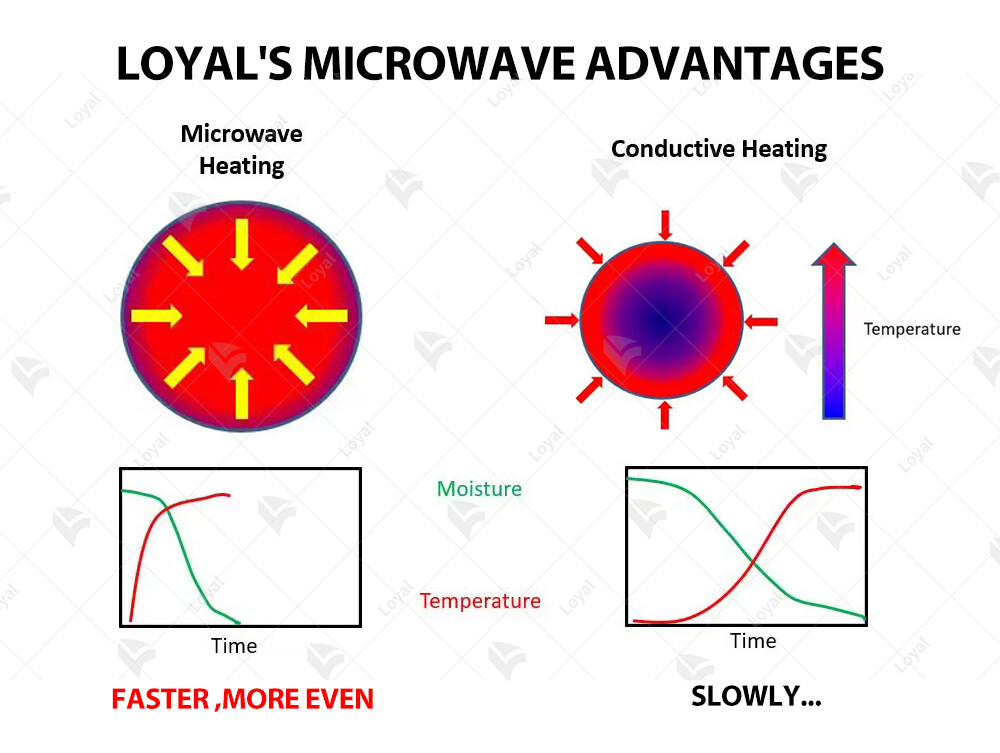
Challenges and Limitations of Industrial Microwave Ovens
Industrial microwave ovens have undoubtedly transformed various sectors of the food industry, offering rapid heating and cooking capabilities. However, despite their many advantages, they are not without challenges and limitations. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing their usage and addressing potential drawbacks.
1. Uneven Heating:
One of the primary challenges associated with industrial microwave ovens is the potential for uneven heating of food products. Due to the nature of microwave technology, certain areas of the food may receive more intense heating than others, resulting in uneven cooking and potential quality issues.
2. Limited Penetration Depth:
Industrial microwave ovens often struggle with achieving consistent heating throughout thicker or denser food products. Microwave energy tends to penetrate only a few centimeters into the food, which can lead to undercooking or overheating of certain areas, particularly in larger or denser items.
3. Product Size and Shape Constraints:
The size and shape of food products can also pose challenges for industrial microwave ovens. Irregularly shaped or oversized items may not receive uniform heating, leading to inconsistencies in cooking results. Additionally, the layout of the oven cavity may limit the types and sizes of products that can be effectively cooked.
4. Moisture Content Variability:
Industrial microwave ovens may struggle with foods that have varying moisture contents. Moisture plays a crucial role in how microwaves interact with food, and products with uneven moisture distribution may cook unevenly or experience texture issues.
5. Energy Consumption and Efficiency:
While industrial microwave ovens are generally more energy-efficient than conventional cooking methods, they still require a significant amount of power to operate. High energy consumption can lead to increased operating costs, particularly for large-scale operations, and may present challenges in terms of sustainability and environmental impact.
6. Equipment Maintenance and Safety:
Maintaining and operating industrial microwave ovens requires specialized training and expertise. These ovens contain high-powered microwave generators and complex control systems, which demand regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and safety. Additionally, there are inherent safety risks associated with microwave radiation, necessitating strict adherence to safety protocols and regulations.
7. Cost Considerations:
Investing in industrial microwave ovens can involve significant upfront costs, including equipment purchase, installation, and training. For some businesses, particularly smaller operations, the initial investment may be a barrier to adoption. Additionally, ongoing operating costs, such as electricity consumption and maintenance, should be carefully considered when evaluating the overall cost-effectiveness of industrial microwave ovens.

References
The following are five authoritative foreign literature websites in the field of industrial microwaves:
1. IEEE Xplore Digital Library
Website: [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/]
2.ScienceDirect
Website: [https://www.sciencedirect.com/]
3. SpringerLink
Website: [https://link.springer.com/]
4. Wiley Online Library
Website: [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/]
5. PubMed
Website: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/]